Beta Decay definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackBeta Decay definitions
1/14
Terms in this set (14)
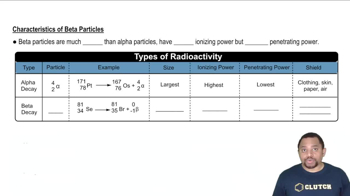
- Beta DecayA nuclear process where an unstable nucleus emits a high-speed electron to convert a neutron into a proton.
- Beta ParticleA high-energy, high-speed electron emitted during beta decay, with negligible mass and negative charge.
- NeutronA subatomic particle in the nucleus with no charge, which can convert into a proton and electron during beta decay.
- ProtonA positively charged subatomic particle in the nucleus, increased in number during beta decay.
- ElectronA negatively charged subatomic particle ejected from the nucleus during beta decay.
- Selenium-81An isotope that undergoes beta decay to transform into bromine-81, maintaining a mass number of 81.
- Bromine-81The product of selenium-81 after beta decay, with an increased atomic number but unchanged mass number.
- Mass NumberThe total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus, unchanged during beta decay.
- Atomic NumberThe number of protons in a nucleus, increased by one during beta decay.
- Ionizing PowerThe ability of a particle to ionize atoms, lower for beta particles compared to alpha particles.
- Penetrating PowerThe ability of a particle to pass through materials, higher for beta particles than alpha particles.
- Alpha ParticleA larger particle compared to beta particles, with higher ionizing but lower penetrating power.
- Helium-4An isotope representing alpha particles, consisting of two protons and two neutrons.
- ShieldingThe use of dense materials like metal or wood to block beta particles due to their penetrating power.