Bases definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackBases definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
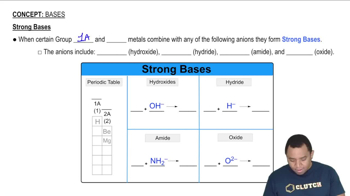
- Group 1A MetalsMetals like lithium, sodium, and potassium that form strong bases with basic anions.
- Group 2A MetalsMetals such as calcium, strontium, and barium that form strong bases with basic anions.
- Basic AnionsAnions like hydroxide, hydride, amide, and oxide that form strong bases with certain metals.
- Hydroxide IonAnion OH- that forms strong bases with certain metals and is a strong proton acceptor.
- Hydride IonAnion H- that forms strong bases with certain metals and is a strong proton acceptor.
- Amide IonAnion NH2- that forms strong bases with certain metals and is a strong proton acceptor.
- Oxide IonAnion O2- that forms strong bases with certain metals and is a strong proton acceptor.
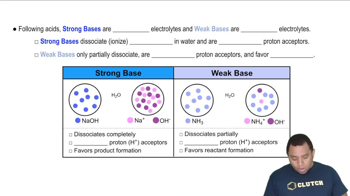
- Strong BasesCompounds that completely dissociate in water and are strong proton acceptors.
- Weak BasesCompounds that partially dissociate in water and are weak proton acceptors.
- ElectrolytesSubstances that dissociate into ions in solution, with strong bases being strong electrolytes.
- Proton AcceptorA substance that readily accepts H+ ions, characteristic of strong bases.
- Neutral AminesCovalent compounds containing nitrogen and hydrogen, acting as weak bases.
- Positive AminesAmines with a positive charge, acting as weak acids.
- Sodium HydroxideA strong base that completely ionizes in water, forming sodium and hydroxide ions.
- AmmoniaA weak base that partially dissociates in water, existing mostly in molecular form.