Band of Stability: Alpha Decay & Nuclear Fission definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackBand of Stability: Alpha Decay & Nuclear Fission definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Radioactive IsotopesUnstable isotopes with an imbalance in neutron and proton numbers, often undergoing decay to achieve stability.
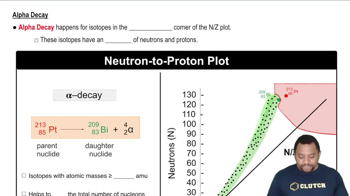
- Alpha DecayA process where an isotope emits an alpha particle to reduce nucleons and move towards stability.
- Nuclear FissionA reaction where an isotope is bombarded with a neutron, splitting into lighter nuclides and releasing energy.
- Band of StabilityA region on the neutron-to-proton plot where stable isotopes reside, with balanced neutron and proton numbers.
- Alpha ParticleA particle consisting of 2 protons and 2 neutrons, emitted during alpha decay.
- NeutronA subatomic particle with no charge, playing a key role in nuclear reactions like fission.
- ProtonA positively charged subatomic particle found in the nucleus, affecting an isotope's stability.
- NucleonsCollective term for protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus.
- Chain ReactionA self-sustaining series of reactions where products initiate further reactions, common in fission.
- Daughter NuclidesStable isotopes produced from the decay or fission of a parent isotope.
- Mega Electron VoltsA unit of energy used to express the energy released in nuclear reactions.
- Neutron-to-Proton PlotA graph showing the relationship between neutrons and protons, indicating stability.
- Parent NuclideThe original unstable isotope that undergoes decay or fission to form daughter nuclides.
- Atomic Mass UnitA unit of mass used to express atomic and molecular weights, crucial in identifying isotopes.
- Electron CaptureA process where an inner orbital electron is captured by the nucleus, altering the isotope's stability.