Atomic Radius & Density of Transition Metals definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackAtomic Radius & Density of Transition Metals definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- Atomic RadiusThe distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell, decreasing gradually across transition metals.
- Transition MetalsElements in the d-block of the periodic table, known for gradual changes in atomic radius.
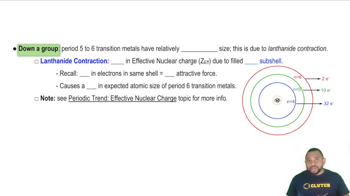
- Lanthanide ContractionA phenomenon where increased effective nuclear charge causes a decrease in atomic size in period 6 transition metals.
- Effective Nuclear ChargeThe net positive charge experienced by electrons, influencing atomic size and density.
- S OrbitalsThe outermost electron orbitals in transition metals, typically holding 1 or 2 electrons.
- D OrbitalsInner electron orbitals in transition metals, where additional electrons are added.
- F OrbitalsInner orbitals in periods 5 and 6, contributing to lanthanide contraction.
- DensityA measure of mass per unit volume, increasing with mass in transition metals.
- PeriodA horizontal row in the periodic table, where atomic radius and density trends are observed.
- GroupA vertical column in the periodic table, where density increases more significantly than across a period.
- Principal Quantum NumberDenoted as n, it represents the shell number of an electron in an atom.
- KryptonA noble gas used as a reference in electron configurations of transition metals.
- XenonA noble gas used in electron configurations, indicating filled inner shells.
- ProtonsPositively charged particles in the nucleus, contributing to effective nuclear charge.
- NeutronsNeutral particles in the nucleus, not affecting the atomic radius directly.