Arrhenius Equation definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackArrhenius Equation definitions
1/10
Terms in this set (10)
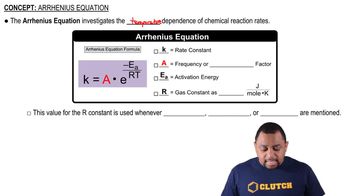
- Arrhenius EquationDescribes how temperature affects reaction rates, involving rate constant, frequency factor, activation energy, gas constant, and temperature.
- Rate ConstantA proportionality constant in the Arrhenius equation that changes with temperature, denoted as k.
- Frequency FactorAlso known as the pre-exponential factor, it represents the frequency of collisions in the Arrhenius equation.
- Activation EnergyThe minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to occur, denoted as Ea in the Arrhenius equation.
- Gas ConstantA constant used in the Arrhenius equation, valued at 8.314 J/(mol·K), denoted as R.
- TemperatureA measure of thermal energy that influences the rate constant in the Arrhenius equation.
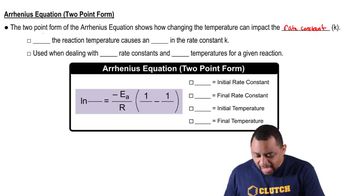
- Two-Point FormA form of the Arrhenius equation used to compare rate constants at two different temperatures.
- Linear FormA rearranged form of the Arrhenius equation used to determine activation energy from a plot of ln(k) vs. 1/T.
- Natural LogarithmThe logarithm to the base e, used in the Arrhenius equation to express the exponential factor.
- Inverse TemperatureThe reciprocal of temperature, used as the x-axis in the linear form of the Arrhenius equation.