Alkane Reactions definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackAlkane Reactions definitions
1/15
Terms in this set (15)
- AlkanesThe least reactive hydrocarbons, primarily undergoing combustion and halogenation reactions.
- HydrocarbonsCompounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- CombustionA reaction where a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
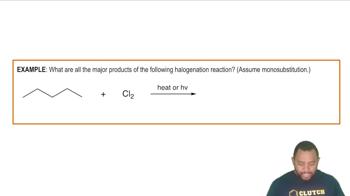
- HalogenationA substitution reaction where a halogen replaces a hydrogen atom in an alkane.
- Alkyl HalidesCompounds formed when a halogen atom replaces a hydrogen atom in an alkane.
- MethaneThe simplest alkane, often used in halogenation reactions as a starting material.
- BromineA halogen that can replace hydrogen in alkanes during halogenation.
- ChlorineA halogen used in halogenation to substitute hydrogen atoms in alkanes.
- Ultraviolet LightEnergy form represented as HV, used to break halogen bonds in halogenation.
- Mono SubstitutionA reaction where only one hydrogen atom in an alkane is replaced by a halogen.
- Poly SubstitutionA reaction where more than one hydrogen atom in an alkane is replaced by halogens.
- Carbon DioxideA product of alkane combustion, formed alongside water.
- WaterA product of alkane combustion, formed alongside carbon dioxide.
- HeatEnergy required to initiate halogenation reactions in alkanes.
- Substitution ReactionA chemical reaction where an atom in a molecule is replaced by another atom.