Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackAlcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions definitions
1/12
Terms in this set (12)
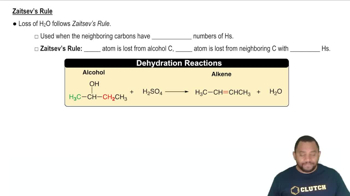
- Dehydration ReactionA process where alcohol is converted to alkene by losing water, typically using sulfuric acid.
- Sulfuric AcidA strong acid (H2SO4) used to facilitate the dehydration of alcohols to form alkenes.
- AlkeneA hydrocarbon containing a carbon-carbon double bond, formed from alcohol dehydration.
- Hydroxyl GroupThe OH group in alcohols that is lost during dehydration to form a double bond.
- Zaitsev's RuleA guideline stating the most substituted alkene is the major product in elimination reactions.
- Double BondA chemical bond where two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms, formed in alkenes.
- Methyl GroupA CH3 group that can be involved in the loss of hydrogen during alcohol dehydration.
- Elimination ReactionA reaction where elements are removed from a molecule, forming a double bond.
- Symmetrical AlcoholAn alcohol where neighboring carbons have the same number of hydrogens, affecting dehydration.
- Unsymmetrical AlcoholAn alcohol with neighboring carbons having different hydrogen counts, influencing product formation.
- Hydrogen AtomAn atom that is lost from a neighboring carbon during the dehydration of alcohols.
- Carbon BondingThe requirement for carbon to maintain four bonds, crucial in forming double bonds in alkenes.