8. Thermochemistry
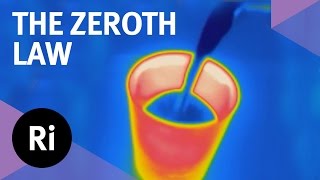
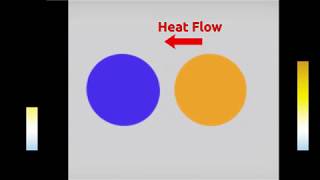
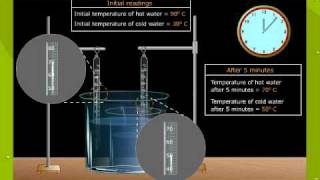
Thermal Equilibrium
8. Thermochemistry
Thermal Equilibrium
Additional 4 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 7 of 7 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
If 53.2 g Al at 120.0 ºC is placed in 110.0 g H2O at 90 ºC within an insulated container that absorbs a negligible amount of heat, what is the final temperature of the aluminum? The specific heat capacities of water and aluminum are 4.184 J/g ∙ ºC and 0.897 J/g ∙ ºC, respectively.
2883views2rank4comments - Open Question
Suppose a 50.0 g block of silver (specific heat = 0.2350 J/g∙°C) at 100°C is placed in contact with a 50.0 g block of iron (specific heat = 0.4494 J/g∙°C) at 0°C, and the two blocks are insulated from the rest of the universe. the final temperature of the two blocks
605views - Multiple ChoiceA 10.69-g block of solid platinum at 66.41°C is immersed in a 23.93-g pool of liquid ethanol with a temperature of 12.95°C. When thermal equilibrium is reached, what is the final temperature of the platinum and ethanol? Specific heat capacities: platinum = 0.133 J/g°C, ethanol = 2.44 J/g°C.270views
- Multiple ChoiceA 14.4 g sample of granite initially at 75.0 °C is immersed into 30.0 g of water initially at 21.0 °C. Assuming the specific heat capacity of granite is 0.79 J/g°C, what is the final temperature of both substances when they reach thermal equilibrium?333views
- Multiple ChoiceA 140.0 g sample of water at 20.0 °C is mixed with 100.0 g of a certain metal at 95.0 °C. After thermal equilibrium is established, the temperature of the mixture is 24.6 °C. What is the specific heat capacity of the metal?270views