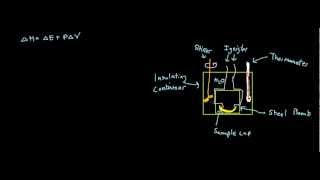
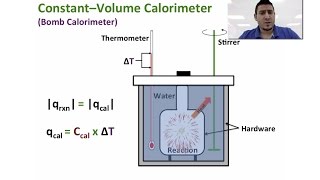
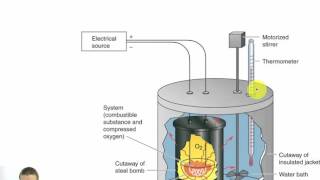
8. Thermochemistry
Constant-Volume Calorimetry
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple ChoiceWhen water evaporates from a beaker at 25℃, 44.0 kJ/mol of heat is required. How much heat is required when 10.0 g of water completely evaporates?
H2O (l) → H2O (g); ΔH = +44.0 kJ/mol
526views - Open Question
A sample of 0.562 g of carbon is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, producing carbon dioxide. assume both the reactants and products are under standard state conditions, and that the heat released is directly proportional to the enthalpy of combustion of graphite. The temperature of the calorimeter increases from 26.74 °C to 27.93 °C. What is the heat capacity of the calorimeter and its contents?
271views - Open Question
When a 0.740-g sample of trinitrotoluene (tnt), C7H5N2O6, is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature increases from 23.4 °C to 26.9 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 534 J/°C, and it contains 675 ml of water. How much heat was produced by the combustion of the tnt sample?
393views - Open Question
Calculate the heat capacity of a calorimeter if the combustion of 5.000g of benzoic acid
382views - Open Question
Calculate the heat capacity of the calorimeter if the combustion of 5.000g of benzoic acid
272views - Multiple ChoiceWhat is the specific heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter if burning 100.0 moles of sulfamic acid results in a temperature increase of 4.57°C, given that the ΔErn for the combustion of 1 mole of sulfamic acid is -686.2 kJ?
- Multiple ChoiceA 2.49 g sample of aniline (C6H5NH2, molar mass = 93.13 g/mol) was combusted in a bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity of 4.25 kJ/°C. If the temperature rose from 29.5 °C to 69.8 °C, determine the value of ΔH°comb for aniline.
- Multiple ChoiceA 21.8 g sample of ethanol (C2H5OH) is burned in a bomb calorimeter, causing the temperature to rise from 25.0°C to 62.3°C. Given that the molar mass of ethanol is 46.07 g/mol, what is the heat capacity of the calorimeter?