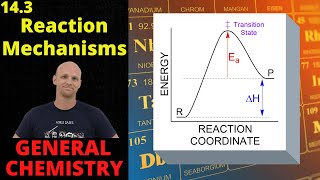
15. Chemical Kinetics
Reaction Mechanism
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Consider the following elementary steps:
NO2 (g) + NO2 (g) → NO3 (g) + NO (g) [SLOW]
NO (g) + CO3 (g) → N (g) + CO4 (g) [FAST]
What is the rate law of the reaction mechanism?
1462views6rank2comments - Multiple Choice
The following reaction of 2 Br2 (g) + 2 NO (g) → N2 (g) + 2 Br2O (g) has the following rate law:Rate = k [Br2][NO]2. The proposed mechanism for the reaction is:
Br2 (g) + NO2 (g) → N (g) + Br2O (g) [SLOW]
N (g) + NO (g) → N2 (g) + O (g) [FAST]
O (g) + Br2 (g) → Br2O (g) [FAST]Which of the following statements is/are false?
a) The rate determining step is bimolecular.
b) There are three elementary steps in the reaction mechanism.
c) The mechanism possesses a catalyst.
d) O is the only reaction intermediate in this reaction mechanism.
e) This is not a valid mechanism for the reaction.1021views1rank - Multiple ChoiceA mechanism for a naturally occurring reaction that destroys ozone is given by the following steps: Step 1: O3(g) + HO(g) → HO2(g) + O2(g) Step 2: HO2(g) + O(g) → HO(g) + O2(g) What is the molecularity of the overall reaction?3views
- Multiple ChoiceConsider the following three-step mechanism for a reaction: Step 1: Cl2(g) ⇌ 2Cl(g) (fast) Step 2: Cl(g) + CHCl3(g) → HCl(g) + CCl3(g) (slow) Step 3: Cl(g) + CCl3(g) → CCl4(g) (fast). Which species are intermediates in this mechanism?2views