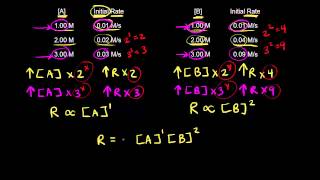15. Chemical Kinetics
Rate Law
15. Chemical Kinetics
Rate Law
Showing 6 of 6 videos
Additional 3 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 6 of 6 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Given the following chemical reaction, A → B. If the concentration of A is doubled the rate increases by a factor of 2.83, what is the order of the reaction with respect to A.
1184views6rank - Multiple Choice
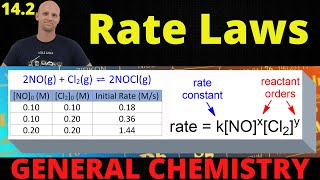
The data below were collected for the following reaction:CH3Cl (g) + 3 Cl2 (g) → CCl4 (g) + 3 HCl (g)
Calculate the value and units for the rate constant k.
1805views6rank2comments - Multiple ChoiceThe concentration of N2O was monitored at a constant temperature as a function of time for the reaction below.
N2O (g) → N2 (g) + ½ O2 (g)
Determine the rate law for this reaction.Reaction Time and Concentration of Nitrous Oxide Time (s) Molar Concentration [N2O] 0 0.500 M 20 0.382 M 40 0.310 M 60 0.260 M 80 0.224 M 432views - Multiple ChoiceUsing the data below (also from questions 6 and 7), determine the value of the rate constant for the reaction.
Data Table for Three Experiments Experiment Initial [NH4+] Initial [NO2] Initial rate (M/s) Experiment 1 0.24 M 0.10 M 7.2 × 10-6 M/s Experiment 2 0.12 M 0.10 M 3.6 × 10-6 M/s Experiment 3 0.12 M 0.15 M 5.4 × 10-6 M/s 463views - Open Question
Consider the rate law. rate=𝑘[a]𝑥 determine the value of 𝑥 if the rate doubles when [a] is doubled.
341views - Open QuestionUsing the data in the table, determine the rate constant of the reaction and select the appropriate units. a+2b⟶c+d492views
- Open QuestionUsing the data in the table, calculate the rate constant of this reaction. a+b⟶c+d1586views
- Open QuestionFor each reaction order, identify the proper units for the rate constant, 𝑘. not all of the choices will be used.502views