15. Chemical Kinetics
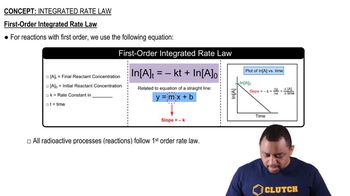
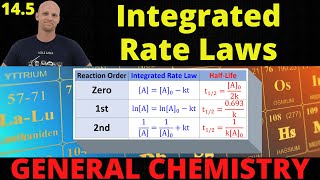
Integrated Rate Law
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
For the reaction A → B, the rate constant is 0.0837 M–1•sec–1. How long would it take for [A] to decrease by 85%?
1210views12rank3comments - Multiple Choice
The following reaction has a rate constant of 3.7 × 10–3 M•s–1 at 25°C:
A → B + C
Calculate the concentration of C after 2.7 × 10–3 sec where [A]0 was 0.750 M at 25°C; assume [C]0 = 0 M.
1193views4comments - Multiple Choice
For the decomposition of urea, NH2CONH2 (aq) + H+(aq) + 2 H2O (l) → 2 NH4+ (aq) + HCO3– (aq), the rate constant is 3.24 × 10–4 s–1 at 35°C. The initial concentration of urea is 2.89 mol/L. What fraction of urea has decomposed after 3.5 minutes?
2026views4rank - Multiple Choice
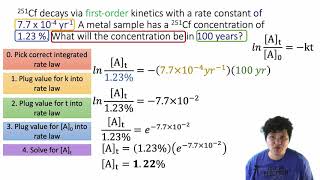
Iodine-123 is used to study thyroid gland function. As this radioactive isotope breaks down, after 5.7 hrs the concentration of iodine-123 is 56.3% complete. Find the rate constant of this reaction.
1312views2rank1comments - Open Question
For the reaction x ⟶ y identify what the graphs of [x] versus time and [y] versus time would look like for various orders. in each graph, [?] represents either [x] or [y].
621views - Open Question
Consider the following general reaction and data: 2a + 2 b + c → d + 3 e
623views