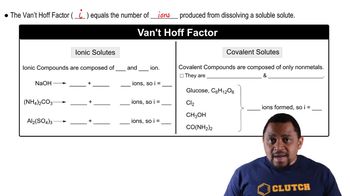
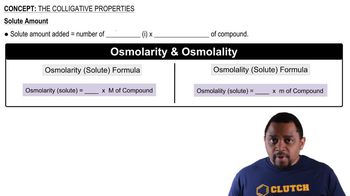
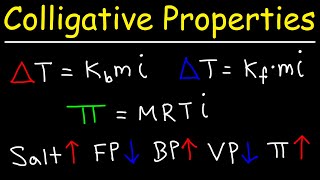
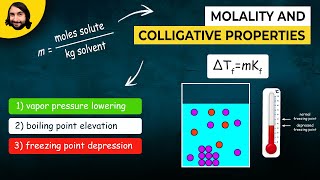
14. Solutions
The Colligative Properties
14. Solutions
The Colligative Properties
Showing 6 of 6 videos
Additional 1 creators.
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following compounds will have the highest boiling point?
1356views3rank1comments - Multiple Choice
Which of the following compound will have the highest vapor pressure?
1161views3rank3comments - Open QuestionAssuming equal concentrations and complete dissociation, arrange these aqueous solutions by their freezing points.723views
- Open Question
Which of the following ions will contribute most to elevating the boiling point of H2O?
556views - Open Question
Explain how the addition of a solute affects the boiling point of a solvent.
542views - Open Question
Why does water boil at a higher temperature than butter, which is non-polar?
743views - Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following best explains why colligative properties are affected differently when a volatile solute is used compared to a nonvolatile solute?25views
- Multiple ChoiceWhich of the following is NOT a colligative property?23views