13. Liquids, Solids & Intermolecular Forces
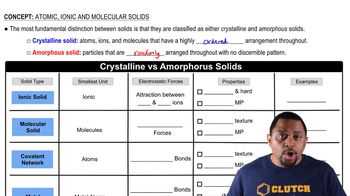
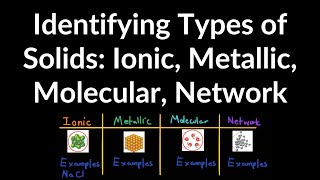
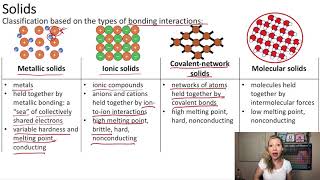
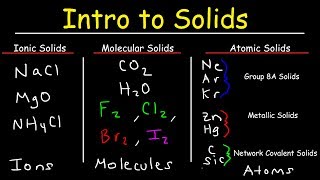
Atomic, Ionic, and Molecular Solids
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
What is the major electrostatic force found between ammonia molecules, NH3?
1022views1rank2comments - Multiple Choice
As it cools off, olive oil slowly hardens and forms a solid over a range of temperatures. Which best describes it as a solid?
1051views6rank1comments - Multiple Choice
Compound A is hard, doesn't conduct electricity, and melts at 1400ºC. Compound A represents which of the following:
751views6rank1comments - Multiple Choice
Classify each solid as amorphous, molecular, network covalent, alloy or ionic.
a) Steel ______________________
b) CO2 ______________________
c) Graphite ______________________
d) CaCO3 ______________________
e) Bronze, an alloy of Cu and Sn ______________________
1243views3rank - Open Question
Which statement best describes why carbon can form a wide variety of organic compounds?
269views - Open Question
Consider the compound Al(OH)3. What type of solid does it form? Crystal lattice, glass, metal, or molecule?
305views - Open Question
What type of crystalline solid is CH3CH2CH2CH3?
428views - Open QuestionAll of the following describes ionic compounds except340views