- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

A molecular model of uric acid is shown in the illustration below. Draw the complete electron-dot structure of uric acid including the lone pairs and multiple bonds, Provide the hybridization of each carbon atom. (gray = C, white = H, red = O, and blue = N)

An incomplete Lewis structure of the nucleobase uracil is shown below. Fill in the missing multiple bonds and lone pairs, then determine the hybridization of the highlighted atoms.

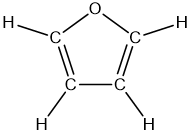
The structure of furan (C4H4O) is shown below. Determine the hybridization of the C atoms and the theoretical value of the C–C=C bond angle. Explain why the actual bond angle is smaller (106 º).
Identify the type of hybridized orbital involved in the diamond lattice.

The following diagram is a representation of the formation of hybrid orbitals by a carbon atom from its 2s and 2p orbitals. The formation of which type of hybrid orbitals is represented by this diagram?

The structure of thiophene is shown below. It is drawn in such a way that each corner represents a carbon atom and the hydrogens are implicit.

Which of the following statement explains why the C–C–C bond angles in benzene are much larger than those in thiophene?
Determine the maximum number of bonds that the following element in a neutral state can form:
Al: [Ne]3s23p1