- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Identify the coordination numbers of the blue atoms, red atoms, and yellow atoms in the following crystal structure.

Crystalline solids are classified into four main classes. List them and provide an example for each.
Consider the two packing patterns below:
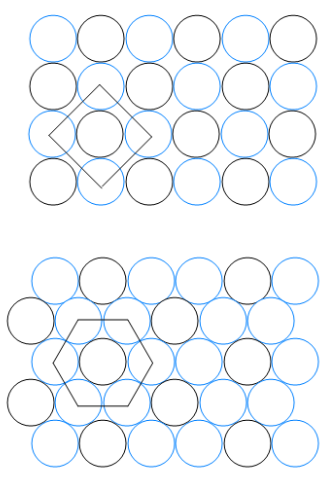
Identify the angle between the lattice vectors.
In an X-ray diffraction analysis, it was found that X-ray from NaCl radiation source has a wavelength of 194 pm. The selected crystalline plane diffracted the radiation at an angle of 25.9 degrees. Assuming that this is second-order diffraction (n = 2) and using the Bragg equation, calculate the spacing between the adjacent crystal planes.
Identify which of the following is expected to have no band gap.
Indicate if the following are n-type or p-type semiconductors
(i) Ge doped with As
(ii) Si doped with B
(iii) Sn doped with Sb
Silicon and germanium are the only two elements that are practically useful semiconductors. However, compound semiconductors that are made from two or more elements are also used. Some examples are CdSe, CdS, GaP, and GaAs.
What is the basis for pairing up these elements? Base your observation on its similarities to Si and Ge.