- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

What makes a hydrofluorocarbon different from a chlorofluorocarbon?
Identify the total number of lone pairs in the structure below:

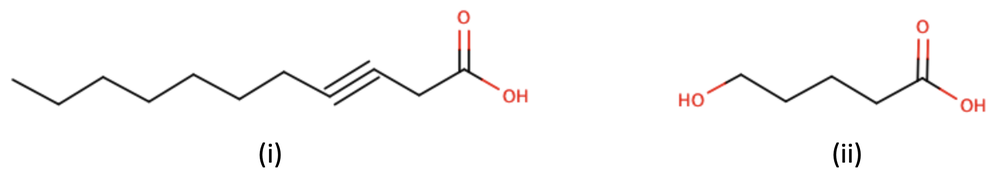
Provide the condensed structures from the given bond line skeletal structures.
Identify the orbitals that overlap for each of the indicated bonds below:

Classify the following molecular formulae as alkanes, alkenes, or alkynes. (Note: It is assumed that these are acyclic, and they can contain only one double or triple bond.)
i) C5H10
ii) C3H4
iii) C6H14
iv) C3H6
The three isomers of dibromo-dichloroethene all have C-C double bonds but are different from one another. Give the Lewis structure of the three isomers of dibromo-dichloroethene.
Are the molecules shown below isomers or identical?

In what ways do isomers differ from each other?
Give the structures of the compounds that exhibit stereoisomerism
i. 2,6‐dimethyl-4-heptanol
ii. 2,5‐dimethyl-4-heptanol
iii. 3,5‐diethyl-4-heptanol
iv. 3,3‐dimethyl-4-heptanol
Is optical isomerism present in the following compound?

Isobutane, (CH3)3CH, is used in refineries to create gasoline-grade compounds. Each carbon atom follows the octet rule, while each hydrogen only forms one bond. The sequence of carbon atoms is shown below. Provide the complete structural formula for isobutane.

Propane used in barbecue grills has a formula C3H8. The carbon atoms are arranged as follows: C–C–C. Draw propane's structural formula given that each carbon forms four covalent bonds.
Give five structural isomers for hexane
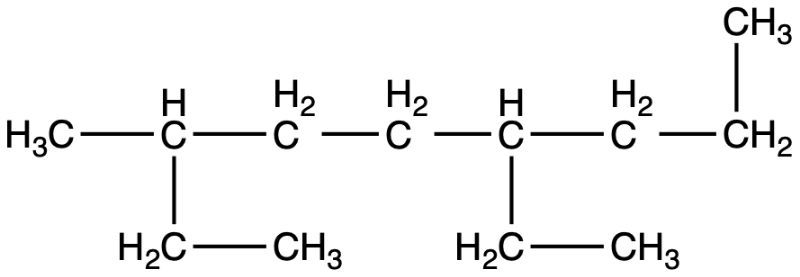
Provide the name of this alkane: