- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

What is the net ionic equation for the dissolution of Cu(OH)2 in NH3? Ksp for Cu(OH)2 is 1.60×10–19 and Kf for [Cu(NH3)4]2+ is 5.60×1011. Determine the equilibrium constant for the dissolution reaction.
When 2.50×10–3 mol of CuCl are added to 450.0 mL of a 0.250 M KCN solution, a complex ion with the formula [Cu(CN)2]– is formed. Kf for the complex ion is 1.00×1016. What is the fraction of uncomplexed Cu+ ions in the solution?
Determine the pH for the following solution: 25.0 mL 0.17 M HIO with 35.0 mL 0.19 M NaIO (Ka HIO = 2.3×10−11)
Identify whether to add KOH or HBr to the buffer mixture to adjust the pH to 9.56. The buffer solution of 1-L initially contains 0.500 M in CH3NH2 and 0.500 M in CH3NH3Br. Calculate the mass of the correct reagent needed.
Acetic acid is a weak acid that dissociates into acetate ion and hydronium ions in solutions:
CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq)
The value of the dissociation constant (Ka) for acetic acid is 1.78×10-5. If you require a buffer of pH 5.25, what would be the ratio of [CH3COO-]/[CH3COOH] that you would use?
The image below shows the titration of a weak base with a strong acid.
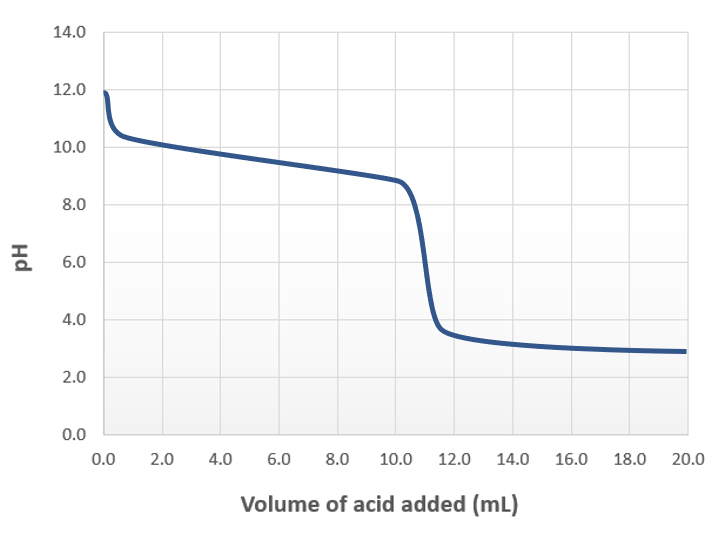
Determine the volume of added acid where the equilibrium concentration of the species in the solution and Ka of the conjugate acid is used to calculate pH.
Various stages of the titration of a weak base, NH3, with a strong acid, HBr, are depicted by the following set of four diagrams. Br– ions and water molecules have been excluded for simplicity.

What is the pH of the solution at the equivalence point?
The titration curve for two monoprotic acids is illustrated below. What is the pKa for the weak acid?

Three unknown acids were titrated against a strong base and the following pH values were noted when the equivalence points were reached:
Acid 1: 7.23
Acid 2: 9.12
Acid 3: 8.57
Which is the strongest and the weakest acid?
HNO3 is a strong acid. When an equal molar amount of KOH is added to an HNO3 solution, an acid-base reaction takes place. Which of the following figures depicts the reaction mixture when the system reaches equilibrium? Note that K+ ions have been omitted for clarity.

At the equivalence point, what is the pH for the titration of 0.15 M HClO and 0.15 M KOH? What is a suitable indicator for the titration? (Ka HClO = 3.0×10−8)

A 0.1164 g sample of an unknown monoprotic acid was dissolved in 35.0 mL of water. A 0.106 M KOH solution was used to titrate the resulting solution. A total of 17.8 mL of KOH was used to reach the equivalence point. The pH of the solution is 9.15 when 8.0 mL of the base was added. Calculate the Ka of the acid.
A diamine is a compound that contains two amino groups and can accept two protons since each nitrogen in the compound can accept a proton. Propylenediamine (1-2-Diaminopropane), H2NC3H6NH2, is an example of a diamine:
H2NC3H6NH2(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3NC3H6NH2+(aq) + OH−(aq) Kb1 = 6.61×10−5
H3NC3H6NH2+(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3NC3H6NH32+(aq) + OH−(aq) Kb2 = 4.07×10−8
Determine the pH of the solution after the addition of the following volumes of 0.300 M HCl to 30.0 mL of 0.200 M propylenediamine.
(i) 0 mL
(ii) 10.0 mL
(iii) 20.0 mL
(iv) 30.0 mL
(v) 40.0 mL
(vi) 50.0 mL