- Download the worksheet to save time writing
- Start solving the practice problems
- If you're stuck, watch the video solutions
- See your summary to get more insights

Consider the diprotic acid, oxalic acid. Identify the chemical equations and the equilibrium expressions for each ionization step.
Choose the correct statement
A 0.135 M solution of diprotic acid H2A has a pH of 5.85. A 0.135 M solution of the salt KHA is basic. Which of the following is a reasonable value for the pKa2 of this acid?
We are given a diprotic acid H2A. It has a Ka1 = 4.2x10-6 and Ka2 = 6.8x10-9
Calculate the pH of 0.0700 M solution of H2A. Calculate the concentrations of H2A and A2- for this solution at equilibrium
The mixture of 0.14 M HCl and 0.19 M HF has a pH of _.
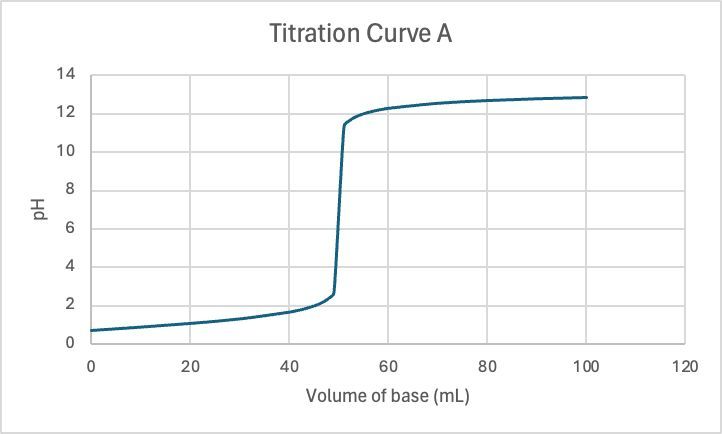
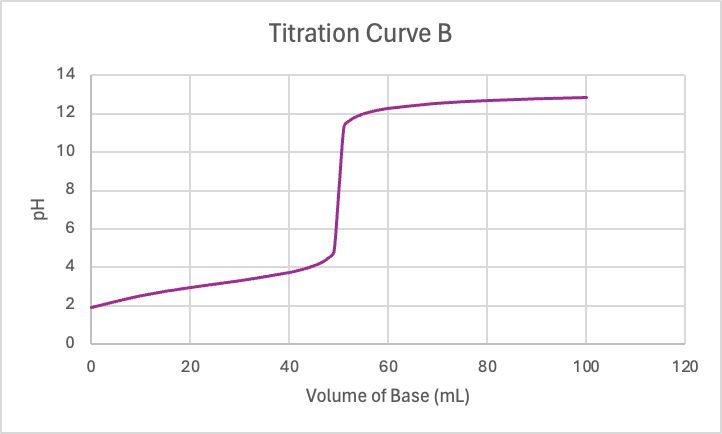
0.200 M KOH is used to titrate 50.0 mL samples of 0.200 M HNO3 and 0.200 M HNO2, individually. Match them to their corresponding titration curve.
Determine the pH and identify the main source of H3O+ in a 1.2 × 10-9 M solution of HCl. Also, determine the pH of 1.2 × 10-7 M HCl. (Hint: pH should not exceed 7.)
Citric acid (HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2) is a weak triprotic acid. Write balanced dissociation equations and corresponding equilibrium expressions for each dissociation step.
Calculate the pH and the molarities of all species (H3AsO4, H2AsO3–, HAsO42–, AsO43–, H3O+, and OH–) in a 9.50 % (by mass) solution of arsenic acid with a density of 1.1033 g/mL. The equilibrium constants are:
Ka1 = 6.46×10–3
Ka2 = 1.14×10–7
Ka3 = 3.16×10–12
What is the pH and [H+] of a 0.24 M H3A (Ka1 = 6.3x10-3, Ka2 = 5.9x10-8, Ka3 = 2.2x10-12) polyprotic acid solution?
Identify whether the compounds are strong acids, weak acids, strong bases, weak bases or, others in an aqueous solution.
CsOH, H2SO4, CH3NH2, HI, CHCOOH, KF, NH3, HCN, H3PO4, Mg(OH)2