Textbook Question
What is the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 10.19 g of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) in enough water to produce 250.0 mL of solution? (LO 4.1) (a) 0.8848 M (b) 18.08 M (c) 1.130 M (d) 0.01808 M
1038
views
1
rank
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
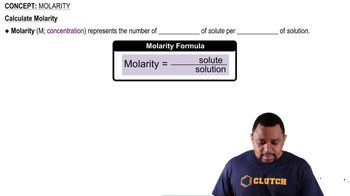


What is the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 10.19 g of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) in enough water to produce 250.0 mL of solution? (LO 4.1) (a) 0.8848 M (b) 18.08 M (c) 1.130 M (d) 0.01808 M