Textbook Question
Give the numerical values of n and l corresponding to each of the following orbital designations: (d) 5d.
791
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


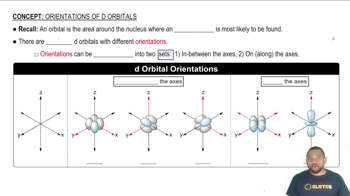
Give the numerical values of n and l corresponding to each of the following orbital designations: (d) 5d.
Give the values for n, l, and 𝑚𝑙 for a. each orbital in the 2p subshell
A certain orbital of the hydrogen atom has n = 4 and l = 2. a. What are the possible values of ml for this orbital?
Which of the following represent impossible combinations of n and l? (a) 1p (b) 4s (c) 5f (d) 2d
For the table that follows, write which orbital goes with the quantum numbers. Don't worry about x, y, z subscripts. If the quantum numbers are not allowed, write 'not allowed.' n l ml Orbital 2 1 -1 2p (example) 1 0 0 3 -3 2 3 2 -2 2 0 -1 0 0 0 4 2 1 5 3 0
Sketch the shape and orientation of the following types of orbitals: (a) s.