Which one of these statements about formal charge is true? (a) Formal charge is the same as oxidation number. (b) To draw the best Lewis structure, you should minimize formal charge. (c) Formal charge takes into account the different electronegativities of the atoms in a molecule. (d) Formal charge is most useful for ionic compounds. (e) Formal charge is used in calculating the dipole moment of a diatomic molecule.
Ch.8 - Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding
Chapter 8, Problem 53b
(b) With what allotrope of oxygen is it isoelectronic?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the term 'isoelectronic': Two species are isoelectronic if they have the same number of electrons.
Identify the allotropes of oxygen: The common allotropes are O2 (dioxygen) and O3 (ozone).
Determine the number of electrons in each oxygen allotrope: O2 has 16 electrons (8 from each oxygen atom) and O3 has 24 electrons (8 from each oxygen atom).
Compare the number of electrons in the given species with the number of electrons in each oxygen allotrope to find which one is isoelectronic.
Conclude which allotrope of oxygen has the same number of electrons as the given species.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
7mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isoelectronic Species
Isoelectronic species are atoms, ions, or molecules that have the same number of electrons and, therefore, the same electronic structure. This concept is crucial for comparing different elements or compounds, as it helps predict their chemical behavior and properties based on their electron configurations.
Recommended video:
Guided course
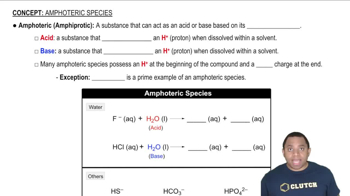
Amphoteric Species
Allotropes of Oxygen
Allotropes are different forms of the same element that exist in the same physical state but have different structures and properties. Oxygen has several allotropes, including dioxygen (O2) and ozone (O3), which exhibit distinct chemical and physical characteristics despite being composed of the same type of atoms.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxyacid Strength Comparison
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in an atom's orbitals. Understanding electron configuration is essential for determining the chemical properties of an element, including its reactivity and how it interacts with other elements, which is particularly relevant when identifying isoelectronic species.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Electron Configuration Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1355
views
Open Question
Write Lewis structures that obey the octet rule for each of the following, and assign oxidation numbers and formal charges to each atom: (a) OCS (b) SOCl2 (S is the central atom) (c) BrO3- (d) HClO2 (H is bonded to O)
Textbook Question
For each of the following molecules or ions of sulfur and oxygen, write a single Lewis structure that obeys the octet rule, and calculate the oxidation numbers and formal charges on all the atoms: (c) SO32- Write a single Lewis structure that obeys the octet rule for SO32- and assign the formal charges on all the atoms.
571
views
Textbook Question
Consider the formate ion, HCO2-, which is the anion formed when formic acid loses an H+ ion. The H and the two O atoms are bonded to the central C atom. (b) Are resonance structures needed to describe the structure?
1828
views
Textbook Question
Predict the ordering, from shortest to longest, of the bond lengths in CO, CO2, and CO32- .
845
views
Textbook Question
Based on Lewis structures, predict the ordering, from shortest to longest, of N¬O bond lengths in NO+, NO2-, and NO3-.
1530
views
1
comments
