Consider the Mg2+, Cl-, K+, and Se2- ions. The four spheres below represent these four ions, scaled according to ionic size. (b) In terms of size, between which of the spheres would you find the (i) Ca2+ and (ii) S2- ions?
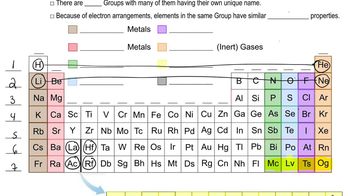
Group 1A and 2A elements are sometimes called, collectively, “the s-block.” Therefore, what is an analogous name for the entire collection of the group 3A, 4A, 5A, 6A, 7A, and 8A elements?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Periodic Table Groups
p-block Elements
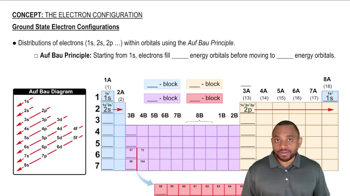
Block Designation in the Periodic Table

In the following reaction
which sphere represents a metal and which represents a nonmetal?
The graph below shows the ionization energies for a particular element. In which group is the element most likely a member of? [Section 7.3]
The prefix eka- comes from the Sanskrit word for 'one.' Mendeleev used this prefix to indicate that the unknown element was one place away from the known element that followed the prefix. For example, eka-silicon, which we now call germanium, is one element below silicon. Mendeleev also predicted the existence of eka-manganese, which was not experimentally confirmed until 1937 because this element is radioactive and does not occur in nature. Based on the periodic table shown in Figure 7.1, what do we now call the element Mendeleev called eka-manganese?
Among elements 1–18, which element or elements have the smallest effective nuclear charge if we use Equation 7.1 to calculate 𝑍eff? Which element or elements have the largest effective nuclear charge?
Which of the following statements about effective nuclear charge for the outermost valence electron of an atom is incorrect? (i) The effective nuclear charge can be thought of as the true nuclear charge minus a screening constant due to the other electrons in the atom. (ii) Effective nuclear charge increases going left to right across a row of the periodic table. (iii) Valence electrons screen the nuclear charge more effectively than do core electrons. (iv) The effective nuclear charge shows a sudden decrease when we go from the end of one row to the beginning of the next row of the periodic table. (v) The change in effective nuclear charge going down a column of the periodic table is generally less than that going across a row of the periodic table
