The maximum allowable concentration of lead in drinking water is 9.0 ppb. (b) How many grams of lead are in a swimming pool containing 9.0 ppb lead in 60 m3 of water?
Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is a polar organic solvent that dissolves a wide range of solutes, including many salts. The density of a 1.80 M LiBr solution in acetonitrile is 0.826 g/cm3. Calculate the concentration of the solution in (c) mass percentage of CH3CN.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
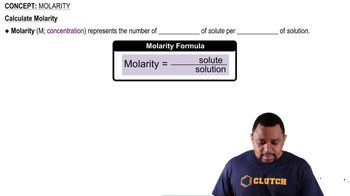
Molarity and Concentration
Mass Percentage

Density and Volume Relationships

Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is a polar organic solvent that dissolves a wide range of solutes, including many salts. The density of a 1.80 M LiBr solution in acetonitrile is 0.826 g/cm3. Calculate the concentration of the solution in (a) molality,
Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is a polar organic solvent that dissolves a wide range of solutes, including many salts. The density of a 1.80 M LiBr solution in acetonitrile is 0.826 g/cm3. Calculate the concentration of the solution in (b) mole fraction of LiBr,
Two beakers are placed in a sealed box at 25 °C. One beaker contains 30.0 mL of a 0.050 M aqueous solution of a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte. The other beaker contains 30.0 mL of a 0.035 M aqueous solution of NaCl. The water vapor from the two solutions reaches equilibrium. (a) In which beaker does the solution level rise, and in which one does it fall?
Two beakers are placed in a sealed box at 25 °C. One beaker contains 30.0 mL of a 0.050 M aqueous solution of a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte. The other beaker contains 30.0 mL of a 0.035 M aqueous solution of NaCl. The water vapor from the two solutions reaches equilibrium. (b) What are the volumes in the two beakers when equilibrium is attained, assuming ideal behavior?
