The alkali metal fulleride superconductors M3C60 have a
cubic closest-packed (face-centered cubic) arrangement of
nearly spherical C60
3- anions with M+ cations in the holes
between the larger C603- ions. The holes are of two types:
octahedral holes, which are surrounded octahedrally by six
C603- ions; and tetrahedral holes, which are surrounded tetrahedrally
by four C603- ions.
(c) Specify fractional coordinates for all the octahedral and
tetrahedral holes. (Fractional coordinates are fractions
of the unit cell edge lengths. For example, a hole at the
center of the cell has fractional coordinates 12, 12, 12.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceRecommended similar problem, with video answer:

Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Cubic Closest-Packed Structure
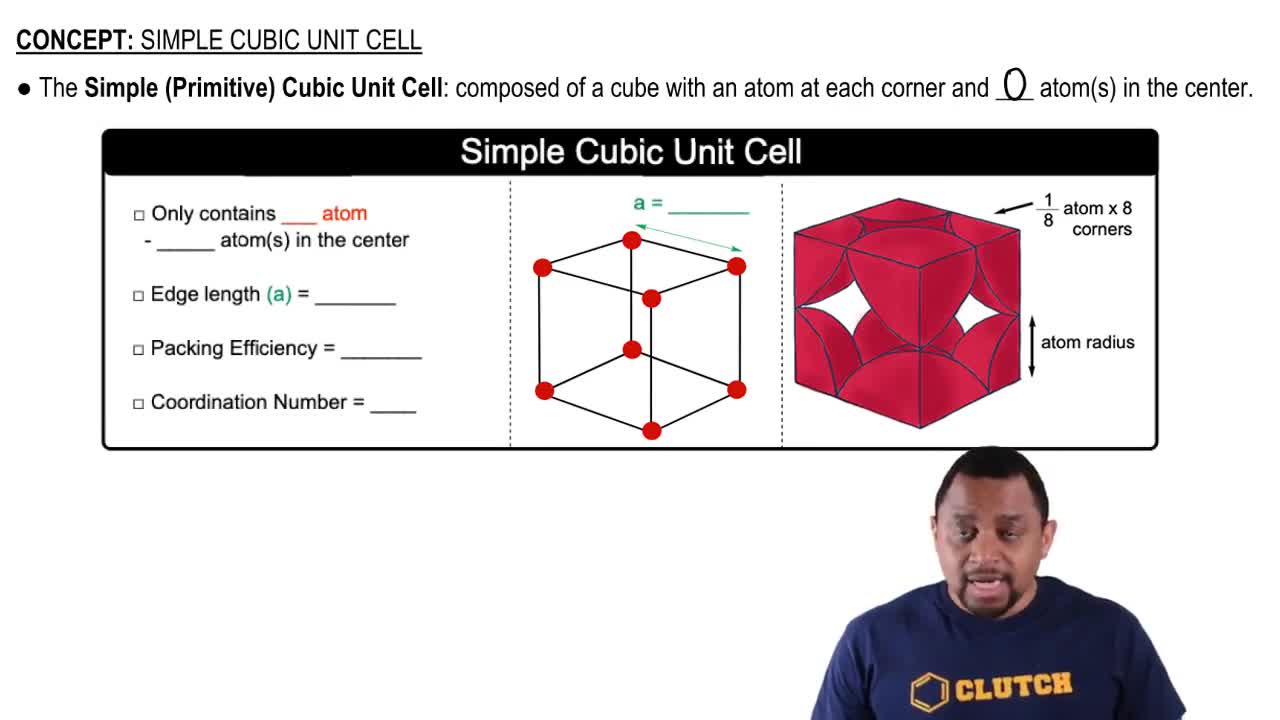
Fractional Coordinates

Octahedral and Tetrahedral Holes
The mineral wustite is a nonstoichiometric iron oxide with the empirical formula FexO, where x is a number slightly less than 1. Wustite can be regarded as an FeO in which some of the Fe sites are vacant. It has a density of 5.75 g>cm3, a cubic unit cell with an edge length of 431 pm, and a facecentered cubic arrangement of oxygen atoms. (c) Each Fe atom in wustite is in either the +2 or the +3 oxidation state. What percent of the Fe atoms are in the +3 oxidation state?
The mineral wustite is a nonstoichiometric iron oxide with the empirical formula FexO, where x is a number slightly less than 1. Wustite can be regarded as an FeO in which some of the Fe sites are vacant. It has a density of 5.75 g>cm3, a cubic unit cell with an edge length of 431 pm, and a facecentered cubic arrangement of oxygen atoms. (d) Using X rays with a wavelength of 70.93 pm, at what angle would third-order diffraction be observed from the planes of atoms that coincide with the faces of the unit cells? Third-order diffraction means that the value of n in the Bragg equation is equal to 3.
Small molecules with C=C double bonds, called monomers, can join with one another to form long chain molecules called polymers. Thus, acrylonitrile, H2C=CHCN, polymerizes under appropriate conditions to give polyacrylonitrile, a common starting material for producing the carbon fibers used in composites. (a) Write electron-dot structures for acrylonitrile and polyacrylonitrile, and show how rearranging the electrons can lead to formation of the polymer.
Small molecules with C'C double bonds, called monomers, can join with one another to form long chain molecules called polymers. Thus, acrylonitrile, H2C'CHCN, polymerizes under appropriate conditions to give polyacrylonitrile, a common starting material for producing the carbon fibers used in composites. (b) Use the bond dissociation energies in Table 7.1 to calculate ΔH per H2C'CHCN unit for the conversion of acrylonitrile to polyacrylonitrile. Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?
