This reaction has an activation energy of zero in the gas phase: CH3 + CH3 → C2H6 a. Would you expect the rate of this reaction to change very much with temperature?

Consider the two reactions:
O + N2 → NO + N Ea = 315 kJ/mol
Cl + H2 → HCl + H Ea = 23 kJ/mol
b. The frequency factors for these two reactions are very close to each other in value. Assuming that they are the same, calculate the ratio of the reaction rate constants for these two reactions at 25 °C.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
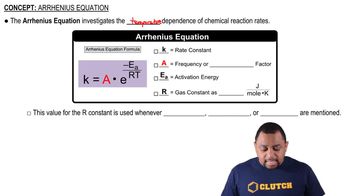
Key Concepts
Arrhenius Equation
Activation Energy (Ea)

Reaction Rate Constant (k)

Consider the two reactions:
O + N2 → NO + N Ea = 315 kJ/mol
Cl + H2 → HCl + H Ea = 23 kJ/mol
a. Why is the activation barrier for the first reaction so much higher than that for the second?
Anthropologists can estimate the age of a bone or other sample of organic matter by its carbon-14 content. The carbon-14 in a living organism is constant until the organism dies, after which carbon- 14 decays with first-order kinetics and a half-life of 5730 years. Suppose a bone from an ancient human contains 19.5% of the C-14 found in living organisms. How old is the bone?
Consider the gas-phase reaction: H2(g) + I2(g) → 2 HI(g) The reaction was experimentally determined to be first order in H2 and first order in I2. Consider the proposed mechanisms. Proposed mechanism I: H2(g) + I2(g) → 2 HI(g) Single step Proposed mechanism II: I2(g) Δk1k-12 I(g) Fast H2( g) + 2 I( g) → k22 HI( g) Slow a. Show that both of the proposed mechanisms are valid.
