Dinitrogen tetroxide decomposes to nitrogen dioxide: N2O4(g) → 2 NO2(g) ΔH°rxn = 55.3 kJ At 298 K, a reaction vessel initially contains 0.100 atm of N2O4. When equilibrium is reached, 58% of the N2O4 has decomposed to NO2. What percentage of N2O4 decomposes at 388 K? Assume that the initial pressure of N2O4 is the same (0.100 atm).
Ch.18 - Free Energy and Thermodynamics
Chapter 18, Problem 100
The Haber process is very important for agriculture because it converts N2(g) from the atmosphere into bound nitrogen, which can be taken up and used by plants. The Haber process reaction is N2(g) + 3 H2(g) → 2 NH3(g). The reaction is exothermic but is carried out at relatively high temperatures. Why?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the Haber process: The Haber process synthesizes ammonia (NH3) from nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2) gases. The balanced chemical equation is N2(g) + 3 H2(g) → 2 NH3(g).
Recognize the nature of the reaction: The reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat.
Consider the effect of temperature on reaction rate: Higher temperatures increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to more frequent and effective collisions, thus increasing the reaction rate.
Apply Le Chatelier's Principle: Although the reaction is exothermic, increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium position to favor the reactants (N2 and H2). However, high temperatures are used to achieve a reasonable reaction rate despite this shift.
Balance between rate and yield: The process is carried out at high temperatures to ensure a faster reaction rate, even though it slightly reduces the yield of ammonia due to the equilibrium shift.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Haber Process
The Haber process is a chemical reaction that synthesizes ammonia (NH3) from nitrogen (N2) and hydrogen (H2) gases. This process is crucial for producing fertilizers, which are essential for modern agriculture. The reaction is represented by the equation N2(g) + 3 H2(g) → 2 NH3(g), highlighting the stoichiometric relationship between the reactants and products.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Born Haber Cycle
Exothermic Reactions
An exothermic reaction is one that releases energy, usually in the form of heat, to its surroundings. In the context of the Haber process, although the reaction itself is exothermic, it is conducted at high temperatures to increase the reaction rate and overcome the activation energy barrier. This is a common practice in industrial chemistry to optimize production efficiency.
Recommended video:
Guided course
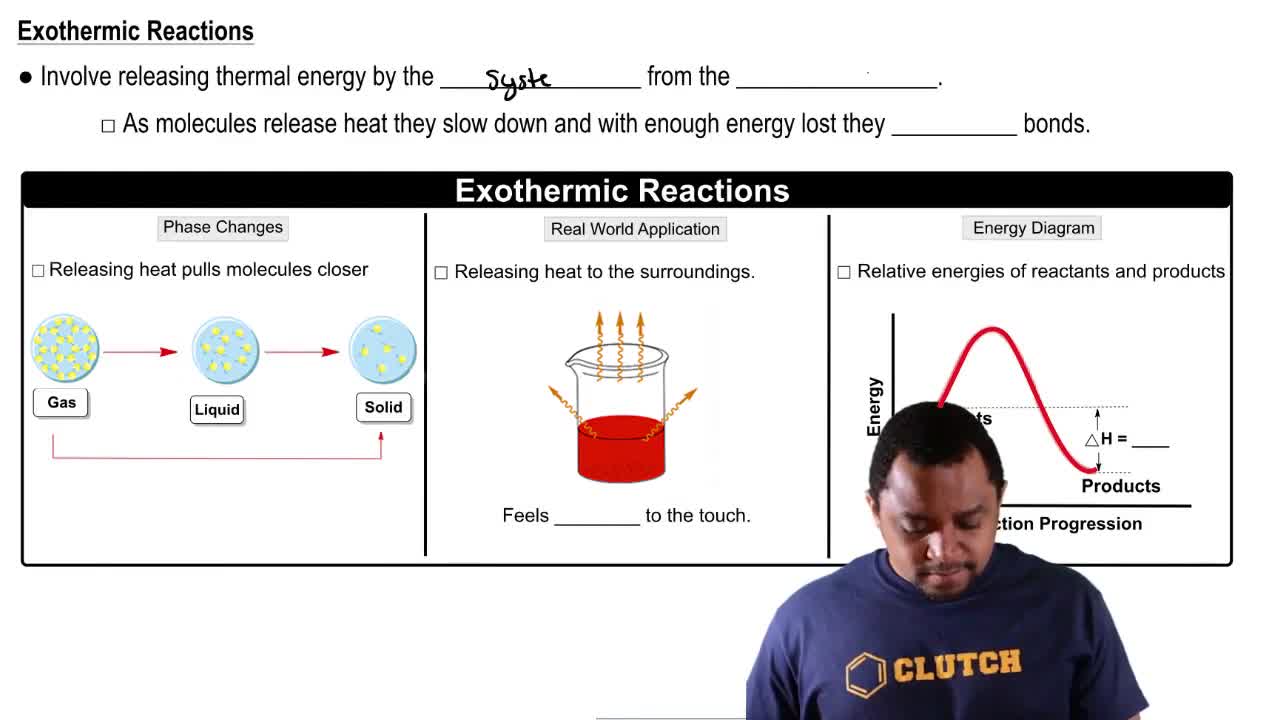
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Le Chatelier's Principle
Le Chatelier's Principle states that if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed by changing the conditions, the system will adjust to counteract the change and restore a new equilibrium. In the Haber process, high temperatures favor the formation of reactants (N2 and H2) over products (NH3), so the reaction is conducted at elevated temperatures to balance the rate of production and maintain efficiency.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Le Chatelier's Principle
Related Practice
Textbook Question
5518
views
2
comments
Open Question
Is the sign of ΔSuniv for each process positive or negative? Explain for the following: b. the electrolysis of H2O(l) to H2(g) and O2(g) at 298 K c. the growth of an oak tree from a little acorn.
Textbook Question
Indicate and explain the sign of ΔSuniv for each process. a. 2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O (l) at 298 K.
549
views
2
comments
Textbook Question
A metal salt with the formula MCl2 crystallizes from water to form a solid with the composition MCl2 • 6 H2O. The equilibrium vapor pressure of water above this solid at 298 K is 18.3 mmHg. What is the value of ΔG for the reaction MCl2 • 6 H2O(s) ⇌ MCl2(s) + 6 H2O(g) when the pressure of water vapor is 18.3 mmHg? When the pressure of water vapor is 760 mmHg?
1503
views
Textbook Question
The solubility of AgCl(s) in water at 25 °C is 1.33⨉10-5 mol/L and its ΔH° of solution is 65.7 kJ/mol. What is its solubility at 50.0 °C?
1910
views
