Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
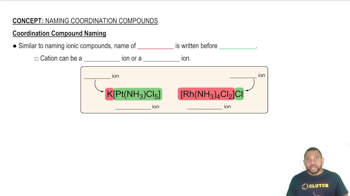
Coordination Compounds
Coordination compounds consist of a central metal atom or ion bonded to surrounding molecules or ions known as ligands. The arrangement and type of ligands influence the properties and geometry of the complex. Understanding the nature of these interactions is crucial for sketching the structure of coordination complexes.
Recommended video:
Coordination Compound Naming
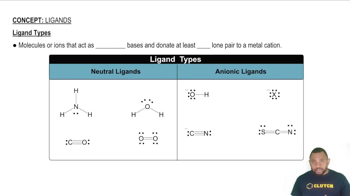
Ligands and Their Types
Ligands are ions or molecules that donate electron pairs to the central metal atom in a coordination complex. They can be classified as monodentate (binding through one atom) or polydentate (binding through multiple atoms). In the given compound, ammonia (NH3) acts as a monodentate ligand, while water (H2O) also serves as a ligand, affecting the overall structure and stability of the complex.
Recommended video:
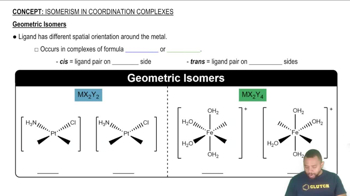
Geometric Isomerism
Geometric isomerism occurs in coordination compounds when ligands can be arranged differently around the central metal atom, leading to distinct spatial configurations. In the case of the compound provided, the 'cis' designation indicates that the ligands are adjacent to each other, which is important for accurately sketching the structure and understanding its chemical behavior.
Recommended video: