Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Orbital Filling Diagram
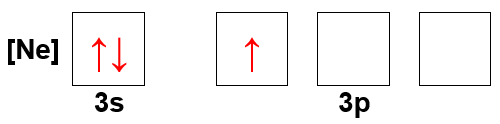
An orbital filling diagram visually represents the distribution of electrons in an atom's orbitals. Each box corresponds to an orbital, and arrows indicate the presence of electrons, with their direction representing spin. The diagram follows the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first, and adheres to Hund's rule, which emphasizes that electrons will occupy degenerate orbitals singly before pairing up.
Recommended video:
Molecular Orbital Diagram
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom's orbitals, typically expressed using a notation that includes the principal quantum number and the type of orbital (s, p, d, f). In the given diagram, the notation [Ne] indicates that the electron configuration starts from the noble gas neon, followed by the filling of the 3s and 3p orbitals. This configuration helps identify the chemical properties and reactivity of the element.
Recommended video:
Electron Configuration Example
Noble Gas Core
A noble gas core refers to the use of a noble gas's electron configuration to simplify the representation of an atom's electron arrangement. In this case, [Ne] signifies that the atom has the same electron configuration as neon, which has a complete outer shell. This notation is useful for quickly identifying the valence electrons and understanding the atom's stability and reactivity, as elements tend to react to achieve a full outer shell.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


