Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding is a strong type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when hydrogen is bonded to highly electronegative atoms like oxygen. In phenol, the hydroxyl (-OH) group can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, enhancing its solubility. Naphthol, while also containing a hydroxyl group, has a larger hydrophobic aromatic ring that limits its ability to interact with water through hydrogen bonding.
Recommended video:
Hydrophobic vs. Hydrophilic Interactions
Hydrophobic interactions refer to the tendency of nonpolar substances to aggregate in aqueous solutions, while hydrophilic interactions involve polar substances that can interact favorably with water. Phenol is more hydrophilic due to its smaller size and ability to form more hydrogen bonds with water, whereas naphthol's larger hydrophobic structure reduces its overall solubility in water.
Recommended video:
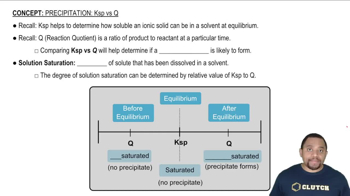
Ksp vs Q in Precipitation
Molecular Size and Structure
The size and structure of a molecule significantly influence its solubility in water. Phenol has a simpler structure with a smaller molecular size compared to naphthol, which has an additional methyl group that increases its hydrophobic character. This structural difference means that phenol can interact more effectively with water, leading to higher solubility.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance