Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Coordination Number
The coordination number refers to the number of ligand atoms that are directly bonded to a central metal atom in a coordination complex. It is a crucial concept in coordination chemistry, as it helps determine the geometry and stability of the complex. For example, a coordination number of 6 typically leads to an octahedral geometry, while a coordination number of 4 can lead to either tetrahedral or square planar geometries.
Recommended video:
Ligands
Ligands are ions or molecules that can donate a pair of electrons to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. They can be classified as monodentate, bidentate, or polydentate based on the number of donor atoms they possess. In the given complexes, fluoride ions (F-) and the EDTA ligand are examples of ligands that coordinate with the metal center, influencing the overall structure and properties of the complex.
Recommended video:
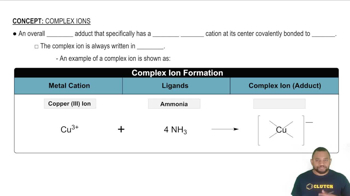
Complex Ions
Complex ions are charged species consisting of a central metal atom bonded to one or more ligands. They can carry a positive or negative charge depending on the nature of the metal and the ligands involved. Understanding complex ions is essential for determining the coordination number, as it directly relates to how many ligands surround the metal center, as seen in the complexes [ZrF8]4- and [Fe(EDTA)(H2O)]-.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance