Textbook Question
Which solid in each pair has the higher melting point and why? d. NaCl(s) or CaO(s)
936
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
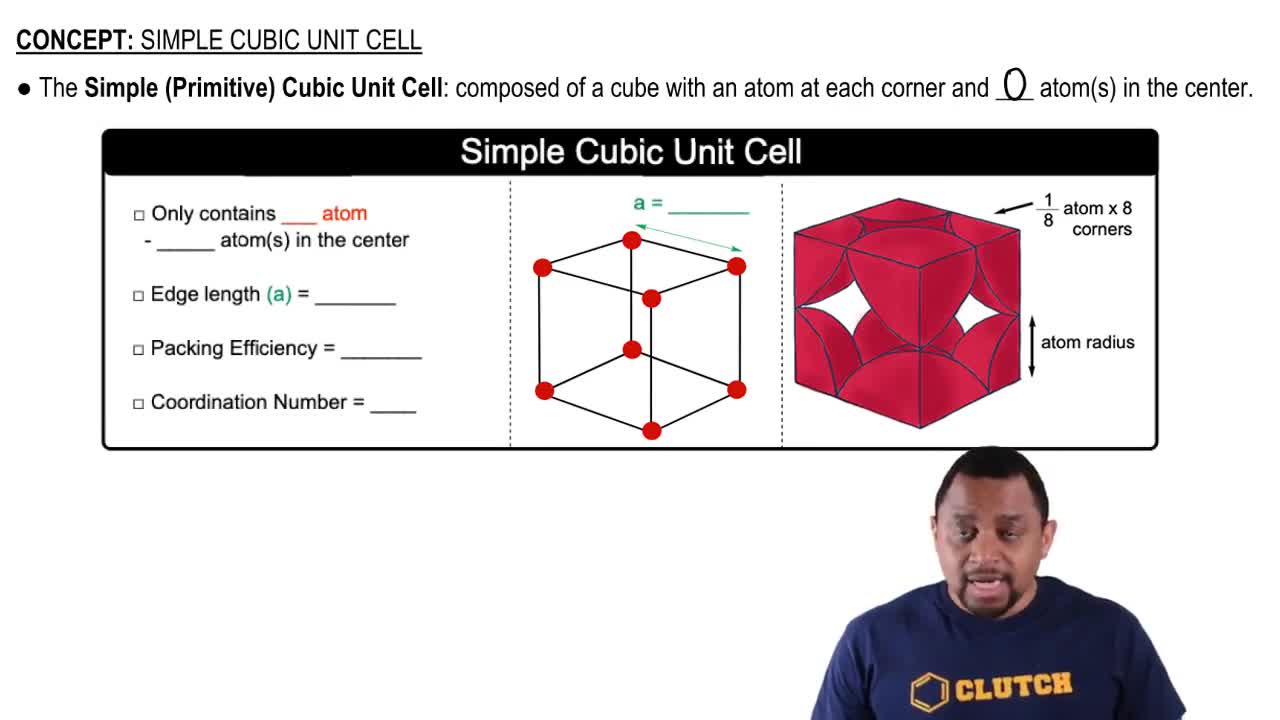


Which solid in each pair has the higher melting point and why? d. NaCl(s) or CaO(s)
Which solid in each pair has the higher melting point and why?
a. Fe(s) or CCl4(s)
b. KCl(s) or HCl(s)
c. Ti(s) or Ne(s)
d. H2O(s) or H2S(s)
An oxide of rhenium crystallizes with the unit cell shown here (rhenium=gray; oxygen=red). What is the formula of the oxide?
Classify each of the following as a component of a silicate ceramic, an oxide ceramic, or a nonoxide ceramic. a. B4C
Classify each of the following as a component of a silicate ceramic, an oxide ceramic, or a nonoxide ceramic. b. Mg2SiO4
Classify each of the following as a component of a silicate ceramic, an oxide ceramic, or a nonoxide ceramic. c. MoSi2