Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law is a fundamental equation in chemistry that relates the pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T), and number of moles (n) of a gas. It is expressed as PV = nRT, where R is the ideal gas constant. This law allows us to predict how a gas will behave under different conditions, making it essential for solving problems involving gas properties.
Recommended video:
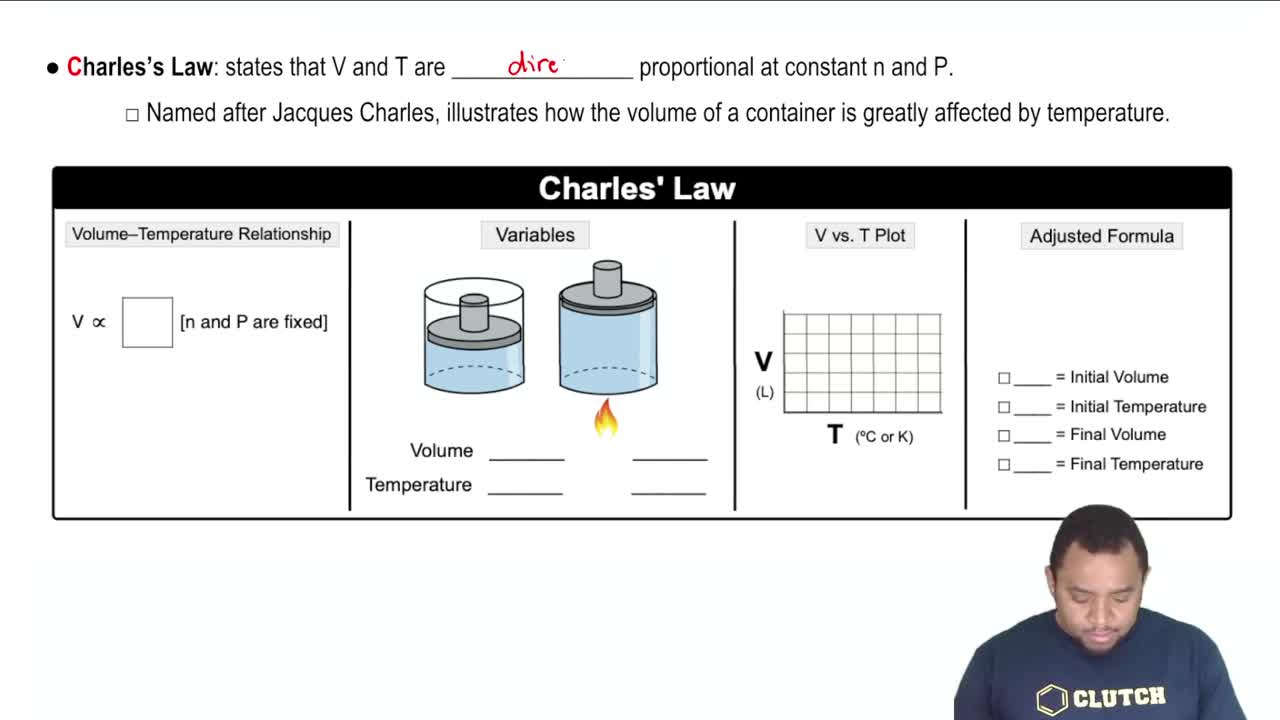
Charles's Law
Charles's Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when pressure is held constant. Mathematically, it can be expressed as V1/T1 = V2/T2. This concept is crucial for understanding how changes in temperature affect the volume of a gas, especially in scenarios where pressure varies.
Recommended video:
Boyle's Law
Boyle's Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas when temperature is held constant. It can be represented as P1V1 = P2V2. This principle is important for analyzing how changes in pressure will influence the volume of a gas, particularly when temperature is not constant.
Recommended video: