Textbook Question
Using Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, calculate the uncertainty in the position of b. a proton moving at a speed of (5.00±0.01) × 104 m/s. The mass of a proton is 1.673×10−27 kg.
1
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

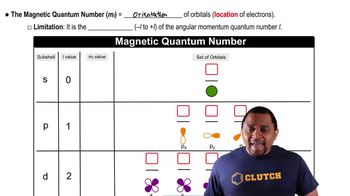

Using Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, calculate the uncertainty in the position of b. a proton moving at a speed of (5.00±0.01) × 104 m/s. The mass of a proton is 1.673×10−27 kg.
Calculate the uncertainty in the position of (a) an electron moving at a speed of 13.00 { 0.012 * 105 m/s
(a) For n = 4, what are the possible values of l?
Give the numerical values of n and l corresponding to each of the following orbital designations: (a) 3p.
Give the numerical values of n and l corresponding to each of the following orbital designations: (d) 5d.
Give the values for n, l, and 𝑚𝑙 for a. each orbital in the 2p subshell