Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electric Charge
Electric charge is a fundamental property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. There are two types of electric charges: positive and negative. Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract. Understanding the nature of electric charge is essential for analyzing the behavior of charged particles in electric fields.
Recommended video:
Electric Field
An electric field is a region around a charged particle where other charged particles experience a force. The direction of the electric field is defined as the direction a positive test charge would move. In the context of the question, the electric field is created by the positively and negatively charged plates, influencing the motion of the charged particle between them.
Recommended video:
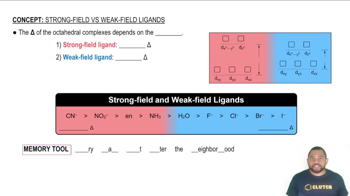
Strong-Field Ligands result in a large Δ and Weak-Field Ligands result in a small Δ.
Force on a Charged Particle
The force acting on a charged particle in an electric field can be described by Coulomb's law, which states that the force is proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The direction of the force depends on the sign of the charge: a positive charge moves toward the negative plate, while a negative charge moves toward the positive plate. This principle is crucial for determining the sign of the charge on the particle in the given scenario.
Recommended video: