Consider the phase diagram for iodine shown here. a. What is the normal boiling point for iodine? b. What is the melting point for iodine at 1 atm? c. What state is present at room temperature and normal atmospheric pressure? d. What state is present at 186 °C and 1.0 atm?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Phase Diagrams
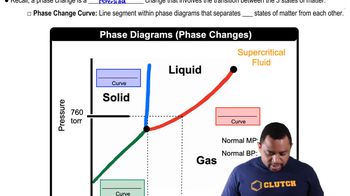
Normal Boiling Point

Melting Point
Consider the phase diagram shown here. Identify the states present at points a through g.
Nitrogen has a normal boiling point of 77.3 K and a melting point (at 1 atm) of 63.1 K. Its critical temperature is 126.2 K and its critical pressure is 2.55×104 torr. It has a triple point at 63.1 K and 94.0 torr. Sketch the phase diagram for nitrogen. Does nitrogen have a stable liquid state at 1 atm?
Argon has a normal boiling point of 87.2 K and a melting point (at 1 atm) of 84.1 K. Its critical temperature is 150.8 K and its critical pressure is 48.3 atm. It has a triple point at 83.7 K and 0.68 atm. Sketch the phase diagram for argon. Which has the greater density, solid argon or liquid argon?
The phase diagram for sulfur is shown here. The rhombic and monoclinic states are two solid states with different structures. a. Below what pressure does solid sulfur sublime?
