Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
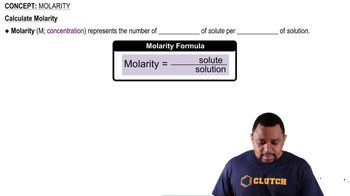
Molarity (M)
Molarity is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. It is expressed in moles per liter (mol/L). Understanding molarity is crucial for calculating the amount of reactants needed in a chemical reaction, as it allows for the conversion between volume and moles.
Recommended video:
Precipitation Reaction
A precipitation reaction occurs when two soluble salts react in solution to form an insoluble salt, known as a precipitate. In this case, silver nitrate reacts with chloride ions to form silver chloride (AgCl), which is insoluble in water. Recognizing the reactants and products in such reactions is essential for determining the stoichiometry involved.
Recommended video:
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions based on the balanced chemical equation. It involves using mole ratios derived from the coefficients of the balanced equation to determine how much of each substance is needed or produced. This concept is vital for solving the problem, as it allows for the calculation of the volume of silver nitrate required to fully react with the chloride ions.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance