Find the total number of atoms in a sample of cocaine hydrochloride, C17H22ClNO4, of mass 23.5 mg.
Ch.3 - Molecules, Compounds & Chemical Equations
Chapter 3, Problem 140
Write the structural formulas of three different compounds that each have the molecular formula C5H12.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify that C5H12 represents an alkane, which is a hydrocarbon with only single bonds between carbon atoms.
Recognize that the different structural formulas represent isomers, which are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements.
Start by drawing the straight-chain isomer, which is n-pentane. This isomer has all five carbon atoms connected in a single, unbranched chain.
Next, draw an isomer with a branching chain. One example is isopentane (also known as 2-methylbutane), which has a four-carbon chain with a methyl group (CH3) attached to the second carbon.
Finally, draw another branched isomer, neopentane (also known as 2,2-dimethylpropane), which has a three-carbon chain with two methyl groups attached to the central carbon.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
8mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where compounds with the same molecular formula exhibit different structural arrangements. In the case of C5H12, there are multiple structural isomers, meaning that the atoms can be connected in various ways, leading to distinct compounds with different properties.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Isomerism in Coordination Complexes Example
Structural Formula
A structural formula represents the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, showing how the atoms are bonded to each other. It provides insight into the connectivity and spatial orientation of the atoms, which is crucial for understanding the chemical behavior and reactivity of the compound.
Recommended video:
Guided course
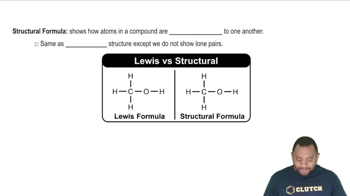
Structural Formula
Alkanes
Alkanes are a class of hydrocarbons characterized by single bonds between carbon atoms and follow the general formula CnH2n+2. The molecular formula C5H12 indicates that the compounds in question are alkanes, specifically pentanes, which can exist in different structural forms such as straight-chain and branched isomers.
Recommended video:
Guided course
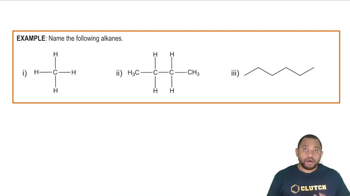
Naming Alkanes Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1226
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
Vanadium forms four different oxides in which the percent by mass of vanadium is, respectively, (a) 76%, (b) 68%, (c) 61%, and (d) 56%. Determine the formula and the name of each oxide.
1103
views
Textbook Question
The chloride of an unknown metal is believed to have the formula MCl3. A 2.395-g sample of the compound contains 3.606×10-2 mol Cl. Find the atomic mass of M.
3338
views
1
rank
1
comments
Open Question
A chromium-containing compound has the formula FexCryO4 and is 28.59% oxygen by mass. Find the values of x and y.
Textbook Question
A phosphorus compound that contains 34.00% phosphorus by mass has the formula X3P2. Identify the element X.
1282
views
Textbook Question
A particular brand of beef jerky contains 0.0552% sodium nitrite by mass and is sold in an 8.00-oz bag. What mass of sodium does the sodium nitrite contribute to the sodium content of the bag of beef jerky?
1303
views
1
comments
