7. Systems of Equations & Matrices
Introduction to Matrices
7. Systems of Equations & Matrices
Introduction to Matrices
Showing 6 of 6 videos
Additional 1 creators.
Learn with other creators
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Write the equations in standard form, then represent the system using an augmented matrix.
232views3rank - Multiple Choice
Perform the indicated Row Operation.
SWAP
170views - Multiple Choice
Perform the indicated Row Operation.
ADD
138views1rank - Multiple Choice
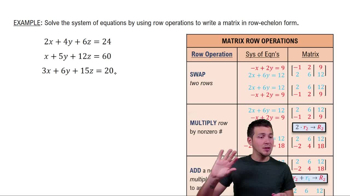
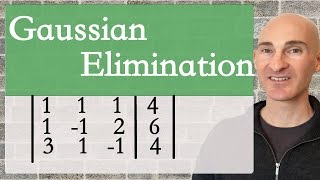
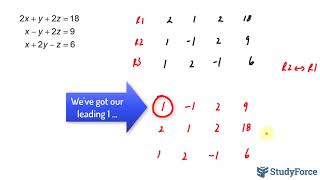
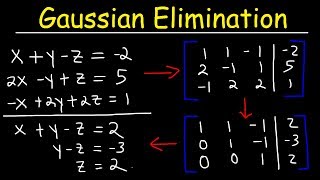
Solve the system of equations by using row operations to write a matrix in REDUCED row-echelon form.
349views - Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–8, write the augmented matrix for each system of linear equations.251views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1–2, perform each matrix row operation and write the new matrix.726views
- Textbook QuestionHow many rows and how many columns does this matrix have? What is its dimension? <4x2 Matrix>200views
- Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1 - 4, a. Give the order of each matrix, b. If A = [a_ij], identify a_32 and a_23, or explain why identification is not possible, 4 - 7 5 - 6 8 - 1 (please enclose the values above in a matrix symbol)278views