Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra(0)
- 1. Equations & Inequalities(0)
- 2. Graphs of Equations(0)
- 3. Functions(0)
- 4. Polynomial Functions(0)
- 5. Rational Functions(0)
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions(0)
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices(0)
- 8. Conic Sections(0)
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction(0)
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability(0)
9. Sequences, Series, & Induction
Sequences
9. Sequences, Series, & Induction
Sequences: Study with Video Lessons, Practice Problems & Examples
65PRACTICE PROBLEM
Prove that the given statement is true for every positive integer n. Use mathematical induction.
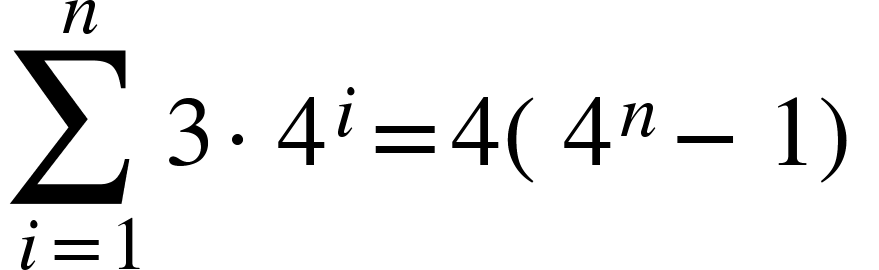
Prove that the given statement is true for every positive integer n. Use mathematical induction.
![]()