Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
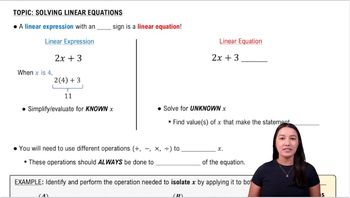
Linear Equations
Problem 10a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionSolve each problem. Which one or more of the following cannot be a correct equation to solve a geometry problem, if x represents the length of a rectangle? (Hint: Solve each equation and consider the solution.) A. 2x+2(x- ) = 14 B. -2x+7(5-x) = 52 C. 5(x+2)+5x = 10 D. 2x+2(x-3) = 22
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Linear Equations
Linear equations are mathematical statements that express the equality of two linear expressions. They typically take the form ax + b = c, where a, b, and c are constants, and x is the variable. Understanding how to manipulate and solve these equations is crucial for determining the possible values of x, especially in geometry problems involving dimensions like length.
Recommended video:

Categorizing Linear Equations
Geometry of Rectangles
In geometry, a rectangle is defined by its length and width, with the area calculated as length multiplied by width. When solving equations related to rectangles, it is essential to ensure that the solutions for x (length) are positive, as negative lengths are not physically meaningful. This context helps in evaluating the validity of the equations provided.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Geometric Sequences - Recursive Formula
Solution Validity
Solution validity refers to the process of checking whether the solutions obtained from an equation make sense within the context of the problem. For instance, in geometry, if a solution yields a negative length for a rectangle, it is deemed invalid. Evaluating the solutions of the given equations against the constraints of the problem is key to identifying which equations are appropriate.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Algebraic Expressions

 7:48m
7:48mWatch next
Master Introduction to Solving Linear Equtions with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice