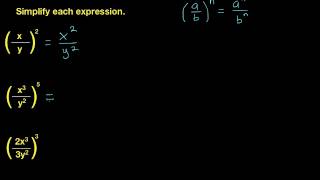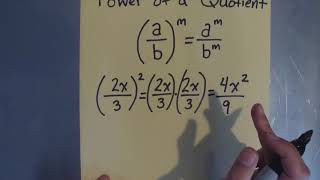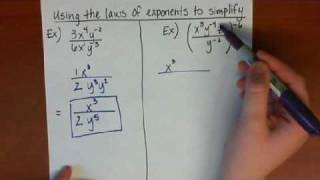Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
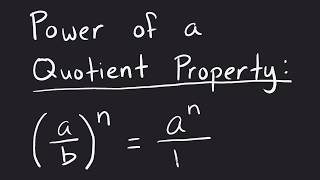
Exponents
Problem 76a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDetermine whether each statement is true or false. {3, 5, 9, 10} ∪ ∅ = {3, 5, 9, 10}
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Set Union
Set union is an operation that combines all unique elements from two or more sets. When performing a union, if an element appears in any of the sets, it will be included in the resulting set. For example, the union of {1, 2} and {2, 3} is {1, 2, 3}.
Recommended video:

Finding the Domain and Range of a Graph
Empty Set
The empty set, denoted as ∅, is a set that contains no elements. It is a fundamental concept in set theory, serving as the identity element for the union operation. When any set is united with the empty set, the result is the original set itself.
Recommended video:

Categorizing Linear Equations
Set Equality
Two sets are considered equal if they contain exactly the same elements, regardless of the order or repetition of those elements. For instance, {1, 2, 3} is equal to {3, 2, 1}. Understanding set equality is crucial for determining the truth of statements involving sets.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation

 7:39m
7:39mWatch next
Master Introduction to Exponent Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice