Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Radical Expressions
Problem 30f
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIf the expression is in exponential form, write it in radical form and evaluate if possible. If it is in radical form, write it in exponential form. Assume all variables represent posi-tive real numbers. (5r + 3t)^4/7
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exponential Form
Exponential form represents numbers using a base raised to a power, indicating repeated multiplication. For example, a number 'a' raised to the power 'n' (a^n) signifies that 'a' is multiplied by itself 'n' times. This form is useful for simplifying calculations and expressing large numbers compactly.
Recommended video:

Exponential Functions
Radical Form
Radical form expresses numbers using roots, such as square roots or cube roots. The radical symbol (√) indicates the root of a number, where 'n'√(a) represents the n-th root of 'a'. Converting between radical and exponential forms allows for different perspectives on the same mathematical expression, facilitating easier manipulation and evaluation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Expanding Radicals
Properties of Exponents and Radicals
Understanding the properties of exponents and radicals is crucial for converting between forms. Key properties include the product of powers (a^m * a^n = a^(m+n)), the power of a power ( (a^m)^n = a^(m*n)), and the relationship between exponents and roots (a^(1/n) = n√(a)). Mastery of these properties enables effective simplification and evaluation of expressions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
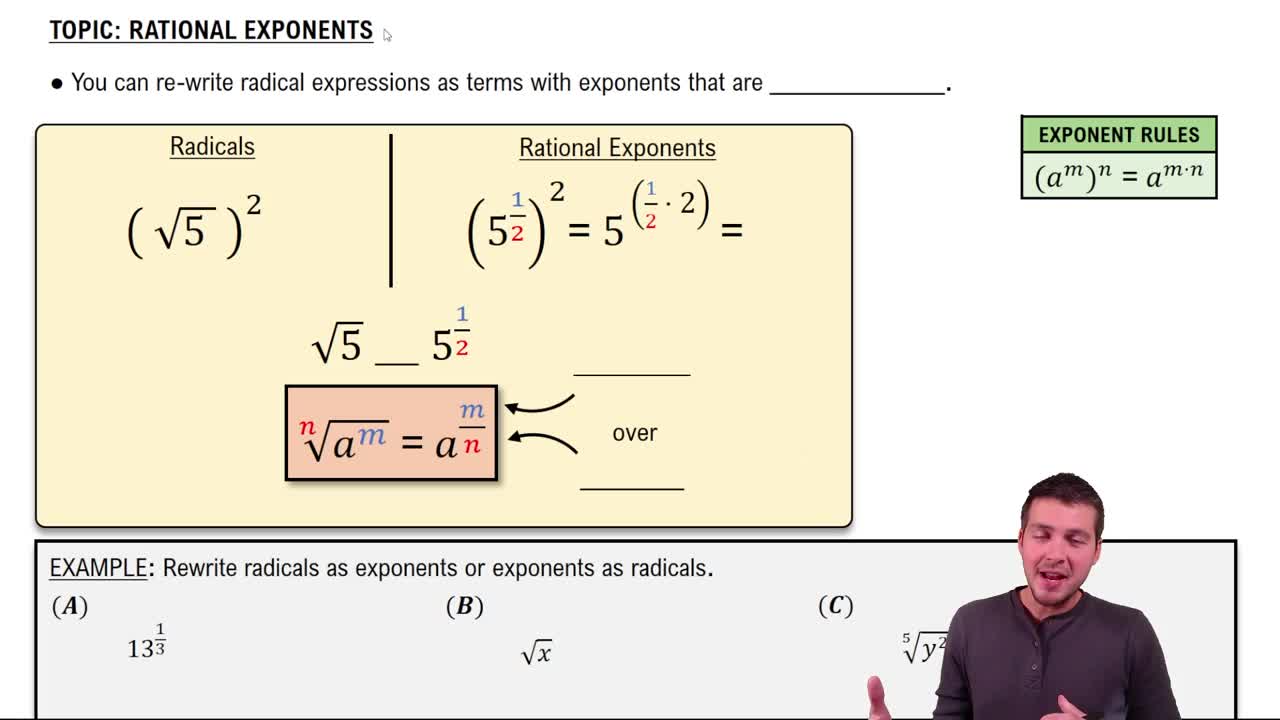
Rational Exponents
Related Videos
Related Practice