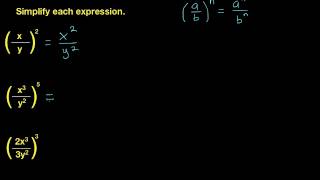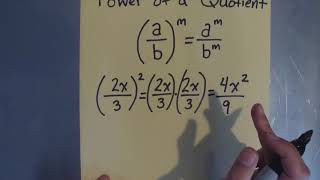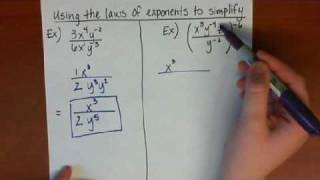Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
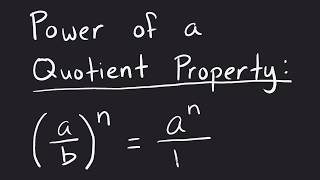
Exponents
Problem 19b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionA football was kicked vertically upward from a height of 4 feet with an initial speed of 60 feet per second. The formula h=4+60t-16t^2 describes the ball's height above the ground, h, in feet, t seconds after it was kicked. Use this formula to solve Exercises 19–20. What was the ball's height 2 seconds after it was kicked?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Quadratic Functions
A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree two, typically expressed in the form f(t) = at^2 + bt + c. In this context, the height of the football is modeled by a quadratic equation, where the term -16t^2 represents the effect of gravity on the ball's height over time. Understanding the properties of quadratic functions, such as their parabolas and vertex, is essential for analyzing the motion of the ball.
Recommended video:

Solving Quadratic Equations Using The Quadratic Formula
Substitution
Substitution is a mathematical technique used to replace a variable with a specific value to evaluate an expression or function. In this problem, we substitute t = 2 seconds into the height formula h = 4 + 60t - 16t^2 to find the ball's height at that specific time. Mastering substitution is crucial for solving equations and understanding how changes in variables affect outcomes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Solving Systems of Equations - Substitution
Projectile Motion
Projectile motion refers to the motion of an object that is thrown or projected into the air, influenced by gravity. The height formula provided captures the essence of projectile motion, where the initial height and speed determine the trajectory of the ball. Recognizing the principles of projectile motion helps in predicting the behavior of objects in free fall and understanding the effects of gravitational acceleration.

 7:39m
7:39mWatch next
Master Introduction to Exponent Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice