Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
5. Rational Functions
Graphing Rational Functions
Problem 84
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionGraph each rational function. See Examples 5–9. ƒ(x)=(x^2+2x+1)/(x^2-x-6)
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
9mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rational Functions
A rational function is a function that can be expressed as the ratio of two polynomials. The general form is f(x) = P(x)/Q(x), where P(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Understanding the behavior of rational functions involves analyzing their domains, intercepts, and asymptotes, which are critical for graphing them accurately.
Recommended video:
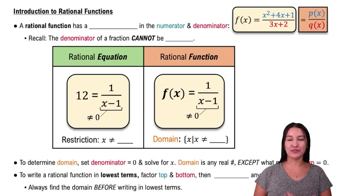
Intro to Rational Functions
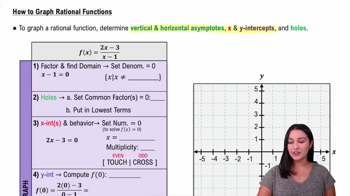
Finding Asymptotes
Asymptotes are lines that the graph of a function approaches but never touches. For rational functions, vertical asymptotes occur where the denominator equals zero (Q(x) = 0), while horizontal asymptotes are determined by the degrees of the polynomials in the numerator and denominator. Identifying these asymptotes is essential for sketching the graph and understanding its behavior at extreme values.
Recommended video:

Introduction to Asymptotes
Factoring Polynomials
Factoring polynomials is the process of breaking down a polynomial into simpler components, or factors, that can be multiplied together to obtain the original polynomial. This is particularly important for rational functions, as it helps simplify the function and identify critical points such as zeros and asymptotes. For example, the function f(x) = (x^2 + 2x + 1)/(x^2 - x - 6) can be factored to facilitate graphing.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Factoring Polynomials

 5:31m
5:31mWatch next
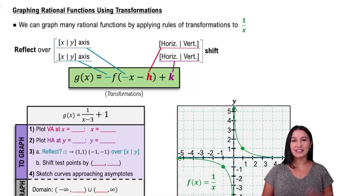
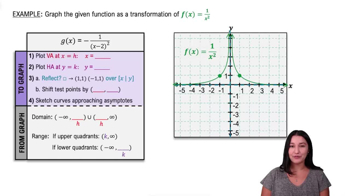
Master Graphing Rational Functions Using Transformations with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice