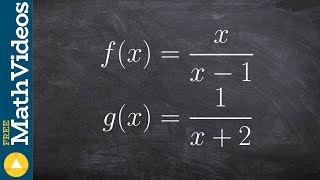Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
3. Functions
Function Composition
Problem 53c
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionFind the inverse of each function that is one-to-one. {(1, -3), (2, -7), (4, -3), (5, -5)}
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
One-to-One Functions
A one-to-one function, or injective function, is a type of function where each output is produced by exactly one input. This means that no two different inputs can map to the same output. Understanding this property is crucial for finding the inverse of a function, as only one-to-one functions have inverses that are also functions.
Recommended video:

Decomposition of Functions
Inverse Functions
An inverse function essentially reverses the effect of the original function. If a function f takes an input x and produces an output y, the inverse function f⁻¹ takes y and returns x. To find the inverse, one typically swaps the roles of the input and output and solves for the new output, ensuring that the function remains one-to-one.
Recommended video:

Graphing Logarithmic Functions
Function Notation and Ordered Pairs
Function notation and ordered pairs are fundamental in representing functions. An ordered pair (x, y) indicates that the function maps input x to output y. When working with functions, especially in finding inverses, it is important to understand how to manipulate these pairs, such as swapping them to find the inverse and ensuring that the resulting pairs still represent a valid function.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation

 4:56m
4:56mWatch next
Master Function Composition with a bite sized video explanation from Nick Kaneko
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice