Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
Choosing a Method to Solve Quadratics
Problem 83
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionSolve each equation. See Example 7. (2x-1)^2/3 = x^1/3
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exponents and Radicals
Understanding exponents and radicals is crucial for solving equations involving powers and roots. In this equation, the term (2x-1) is raised to the power of 2/3, which indicates both squaring the expression and taking the cube root. Similarly, x^1/3 represents the cube root of x. Mastery of these concepts allows for proper manipulation and simplification of the equation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
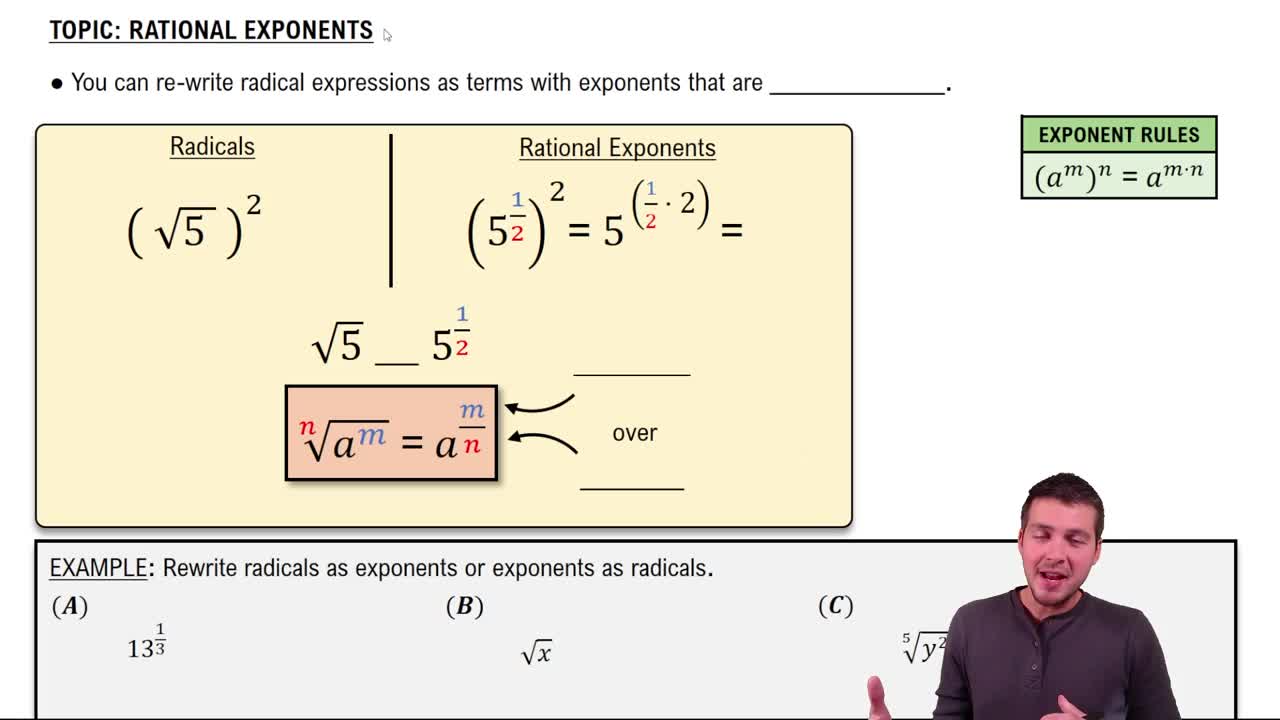
Rational Exponents
Isolating Variables
Isolating variables is a fundamental technique in algebra that involves rearranging an equation to solve for a specific variable. In this case, you will need to manipulate the equation to isolate x. This often includes applying inverse operations, such as raising both sides to a power or moving terms across the equation, which is essential for finding the solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Equations with Two Variables
Checking Solutions
After solving an equation, it is important to check the solutions to ensure they satisfy the original equation. This step helps identify any extraneous solutions that may arise from the manipulation of the equation, especially when dealing with roots and powers. Verifying solutions ensures accuracy and confirms that the derived values are valid within the context of the problem.
Recommended video:

Restrictions on Rational Equations

 4:03m
4:03mWatch next
Master Choosing a Method to Solve Quadratics with a bite sized video explanation from Callie
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

