Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
7. Systems of Equations & Matrices
Introduction to Matrices
Problem 11e
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn Exercises 1 - 24, use Gaussian Eliminaion to find the complete solution to each system of equations, or show that none exists. 2w + x - y = 3 w - 3x + 2y = - 4 3w + x - 3y + z = 1 w + 2x - 4y - z = - 2
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
12mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gaussian Elimination
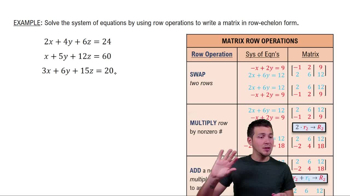
Gaussian elimination is a method for solving systems of linear equations. It involves transforming the system's augmented matrix into row echelon form using a series of row operations, which simplifies the equations. Once in this form, back substitution can be used to find the values of the variables. This technique is essential for determining whether a unique solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solution exists.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Solving Systems of Equations - Elimination
Row Operations
Row operations are the fundamental manipulations used in Gaussian elimination to simplify matrices. These include swapping two rows, multiplying a row by a non-zero scalar, and adding or subtracting a multiple of one row to another. Understanding these operations is crucial, as they maintain the equivalence of the system while allowing for easier computation and solution finding.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Performing Row Operations on Matrices
Augmented Matrix
An augmented matrix is a matrix that represents a system of linear equations, including the coefficients of the variables and the constants from the equations. It is formed by appending the constant terms as an additional column to the coefficient matrix. This representation is vital for applying Gaussian elimination, as it allows for a compact and systematic approach to solving the system.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Matrices

 4:35m
4:35mWatch next
Master Introduction to Matrices with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice