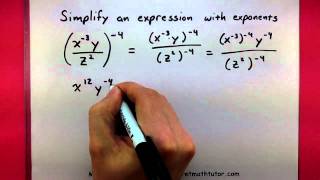Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 16m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 6m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 19m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
0. Review of Algebra
Exponents
Problem 109
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionLet U = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13}, M = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8}, N = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13}, Q = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12}, and R = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4}.Use these sets to find each of the following. Identify any disjoint sets. {x | x ∈ M or x ∈ Q}
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Sets and Set Notation
A set is a collection of distinct objects, considered as an object in its own right. Set notation uses curly braces to define a set, with elements separated by commas. Understanding how to read and write sets is crucial for manipulating them, such as identifying unions, intersections, and differences between sets.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation
Union of Sets
The union of two sets combines all unique elements from both sets. It is denoted by the symbol '∪'. For example, if M = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8} and Q = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12}, the union M ∪ Q includes all elements from both sets without duplication, resulting in {0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12}.
Recommended video:

Finding the Domain and Range of a Graph
Disjoint Sets
Disjoint sets are sets that have no elements in common, meaning their intersection is the empty set. For instance, if M = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8} and N = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13}, these sets are disjoint because they do not share any elements. Identifying disjoint sets is important for understanding relationships between different collections of objects.
Recommended video:

Interval Notation

 7:39m
7:39mWatch next
Master Introduction to Exponent Rules with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick Ford
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice