Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exponential Functions
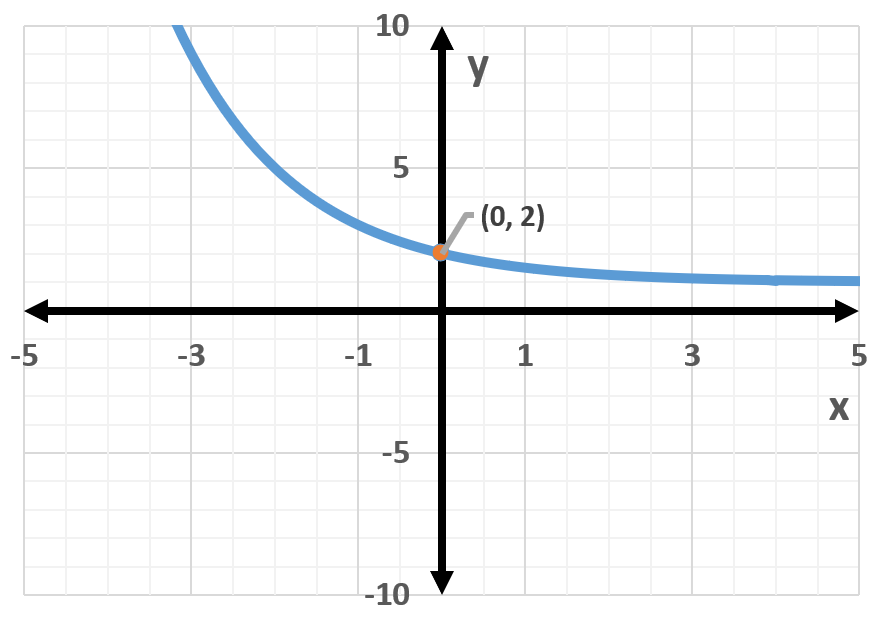
Exponential functions are mathematical expressions in the form f(x) = a^x, where 'a' is a positive constant. These functions exhibit rapid growth or decay, depending on whether 'a' is greater than or less than 1. The graph of an exponential function is characterized by a continuous curve that approaches the x-axis but never touches it, known as a horizontal asymptote.
Recommended video:
Graph Characteristics
The graph of an exponential function has distinct characteristics, including a y-intercept at (0, a) and a horizontal asymptote along the x-axis. If the base 'a' is greater than 1, the function increases as x increases; if 'a' is between 0 and 1, the function decreases. The steepness of the curve is influenced by the value of 'a', with larger bases resulting in steeper growth.
Recommended video:
Graphs and Coordinates - Example
Transformations of Functions
Transformations of functions involve shifting, reflecting, or stretching the graph of a function. For example, a negative exponent indicates a reflection across the y-axis, while adding a constant shifts the graph vertically. Understanding these transformations is crucial for identifying the correct function that matches a given graph, as they alter the basic shape and position of the exponential function.
Recommended video:
Domain & Range of Transformed Functions
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

